An Alarming Cybersecurity Breach: 183 Million Email Passwords Exposed
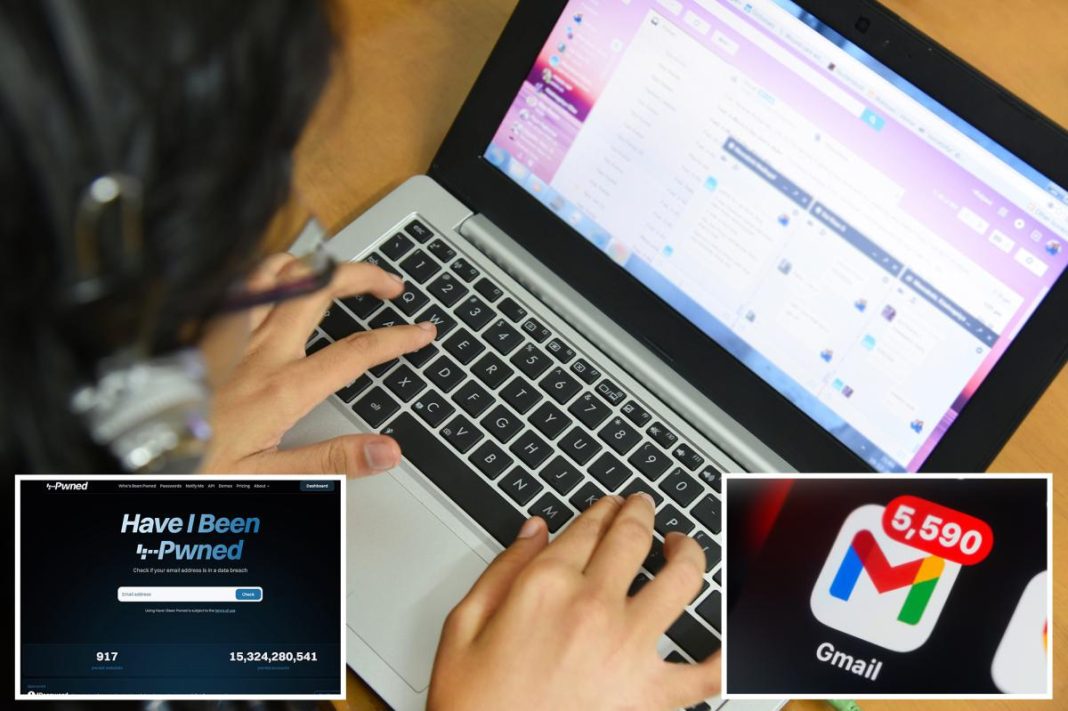
In a shocking revelation, a significant data breach has led to the exposure of over 183 million email passwords, with a particular focus on those associated with Gmail accounts. This staggering leak, described by cybersecurity experts as one of the largest credential dumps ever identified, has raised alarm bells across the tech community. Troy Hunt, an Australian security researcher and creator of the breach-notification website Have I Been Pwned, reported that this extensive dataset containing around 3.5 terabytes of data surfaced online recently, highlighting the severity of the situation. The breach has not only impacted individual users but has also cast a shadow over the integrity of online security as a whole, raising questions about the measures in place to protect sensitive user data.

According to Hunt, the exposed data originates from a year-long investigation into “infostealer” platforms—sophisticated malware networks designed to covertly capture usernames, passwords, and URLs from compromised devices. These infostealer platforms operate in the dark corners of the internet, utilizing advanced techniques to evade detection while gathering vast amounts of personal data. This particular leak not only comprises stolen email credentials but is also categorized into “stealer logs and credential stuffing lists.” These lists are vital for cybercriminals, as they outline the stolen data that can be exploited for unauthorized access to various online services, including banking and e-commerce. The readiness with which this data is traded underscores a thriving underground economy that poses a persistent threat to users everywhere.

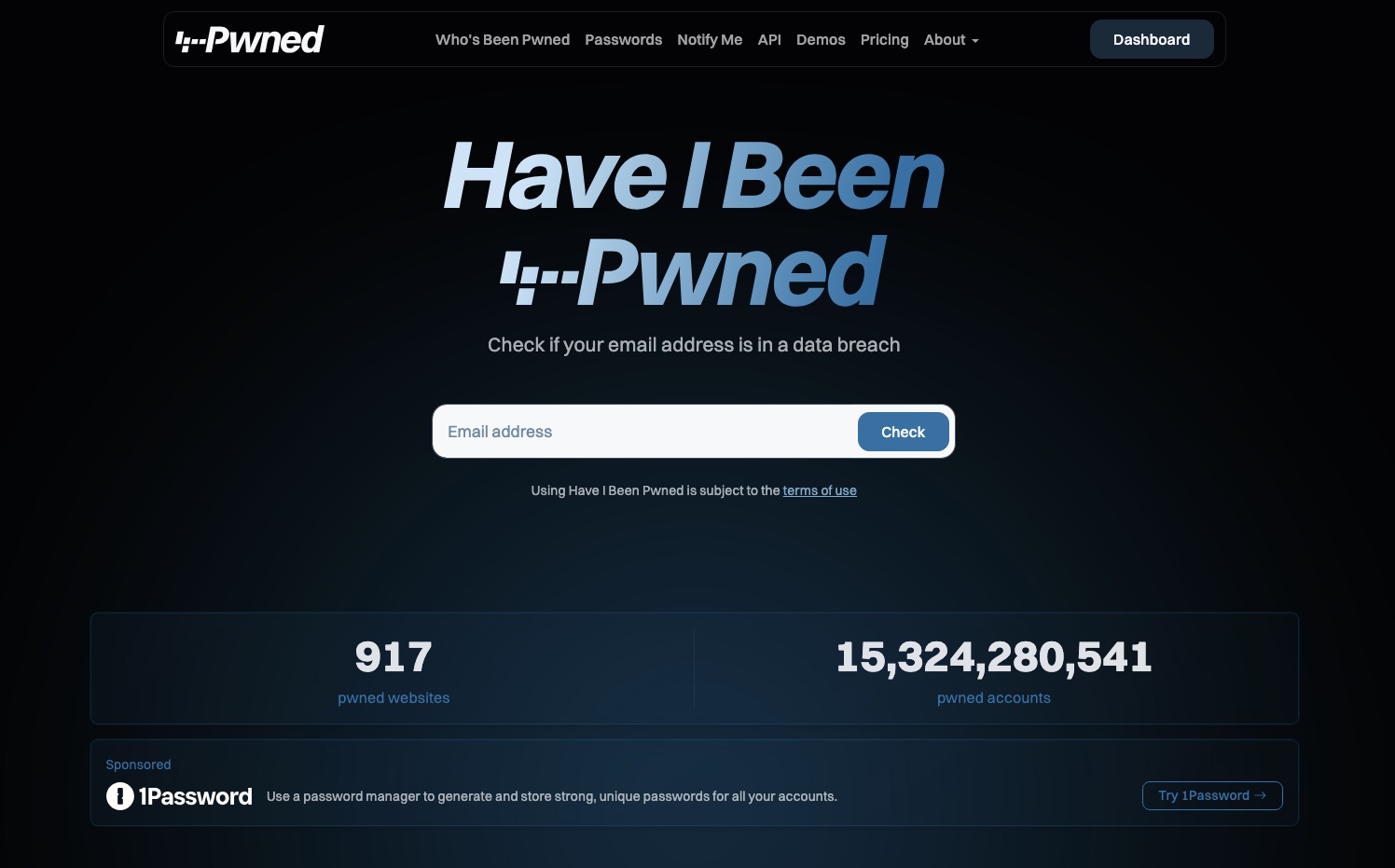
The dataset unearthed during this breach includes a staggering 183 million unique accounts, marking a significant increase in the number of compromised credentials compared to prior breaches. Hunt noted that among the leaked accounts, approximately 16.4 million had never been part of any previous data leaks, underscoring the fresh risks posed to users. For individuals concerned about their account security, Have I Been Pwned offers an invaluable tool; users can input their email addresses to check if their credentials have been compromised, along with details regarding the breach. This proactive approach empowers users, enabling them to take immediate steps toward securing their accounts and minimizing potential damage before it’s too late.

The Mechanisms of Credential Theft
Security firm Synthient, which played a role in collecting and analyzing the logs, revealed that the compromised records were sourced from underground marketplaces and channels on Telegram, where hackers frequently share stolen credentials. Analyst Benjamin Brundage highlighted the widespread implications of infostealer malware, noting that while many of the leaked entries are recycled from older breaches, a significant number of new Gmail accounts were confirmed as compromised when users acknowledged that their passwords matched those exposed in the leak. This indicates a concerning trend: even new users are at risk due to the prevalence of stolen information circulating freely in underground networks.

This recent breach, detected initially in April and made public shortly afterward, not only affects Gmail users but also encompasses login information for various platforms such as Outlook, Yahoo, and countless other online services. Hunt pointed out that this incident is indicative of a larger problem: stolen credentials often resurface across multiple forums over time, granting cybercriminals an ongoing opportunity to exploit reused passwords. It is essential to comprehend that the breaches did not arise from a direct hack of Gmail itself; instead, they were facilitated through malware installed on users’ devices that effectively captured their login data. This critical distinction emphasizes the importance of device security as a frontline defense against cyber threats.
Understanding the Broader Implications
Cybersecurity experts have voiced urgent calls for Gmail users to take immediate action to secure their accounts. If you are among the 183 million individuals affected, it is imperative to change your email password immediately and activate two-factor authentication if you have not already done so. British security analyst Michael Tigges emphasized that while the attack did not directly breach Gmail, it serves as a crucial reminder for users to scrutinize how they manage their online credentials. “This event underscores the importance of avoiding shared passwords across different services,” Tigges stated. In practical terms, this means that users should adopt a mindset of vigilance and responsibility when it comes to their online security.

Echoing similar sentiments, security blogger Graham Cluley advised that individuals should utilize unique passwords for each online account and store them using secure, encrypted password managers instead of relying on web browsers, which are susceptible to malware. Password managers not only facilitate the creation of strong, complex passwords but also help users avoid the pitfalls of forgotten credentials. Google has also introduced tools such as the Password Manager Checkup, which scans saved logins in Chrome and alerts users to any weak or reused credentials. The company’s proactive measures include automatic prompts for password resets when significant credential dumps are discovered. This highlights the role of major tech companies in safeguarding user data through innovative solutions.

Preventing Future Breaches
Research indicates that a majority of the compromised credentials were likely obtained through malicious software downloads, phishing emails, or deceptive browser extensions. Often, victims remain unaware that their devices have been compromised, making it crucial to adopt preventive measures. Ensuring that your antivirus software is up to date and downloading applications from reputable sources are fundamental steps in thwarting potential malware attacks. As Tigges noted, “Prevention is the chief mitigation,” emphasizing the need for vigilance when it comes to personal cybersecurity. Regularly updating software and being cautious about what to click on in emails are practices that can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to cyber threats.

While the scale of this recent data dump is indeed alarming, Troy Hunt cautioned against complacency. He reiterated that reusing passwords across different platforms is a recipe for disaster, potentially enabling attackers to exploit this database for months or even years. By selling verified Gmail logins to fraud networks, cybercriminals can significantly increase the risk posed to individuals who fail to adopt robust cybersecurity practices. The onus is on users to take these warnings seriously and implement multifaceted security strategies that address both technological and behavioral aspects of online safety.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The recent exposure of 183 million email passwords serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities present in our digital lives. It highlights the necessity for users to remain vigilant and proactive in protecting their online information. By adopting secure password management practices, enabling two-factor authentication, and staying informed about the latest cybersecurity threats, individuals can better safeguard their accounts against potential breaches. The responsibility of securing personal data lies not only with service providers but also with users themselves, making it imperative to prioritize cybersecurity in an increasingly interconnected world. This incident is a wake-up call, urging everyone to reconsider their digital habits and take the necessary steps to fortify their online presence.