The Hidden Dangers of Reheating Certain Foods
As our lives become increasingly busy and fast-paced, the trend of meal-prepping has gained significant popularity among individuals seeking to save time and maintain a healthy diet. Preparing meals in advance can indeed streamline daily routines and help manage nutritional intake; however, it is crucial to recognize that not all foods are suitable for reheating. Some foods pose serious health risks if stored or reheated improperly, leading to potential foodborne illnesses or even long-term health complications. Understanding these risks is essential for anyone who enjoys the convenience of prepared meals.
Understanding the Risks of Meal Prepping
When we think about meal prep, we often envision convenient, healthy options ready for consumption. However, the reality is more complicated. Foods can develop harmful bacteria or toxic compounds when they are stored improperly or reheated. These issues can arise from a lack of understanding about how certain ingredients interact with high temperatures or extended storage times. This article aims to highlight some common foods that should never be reheated and explain the reasons behind these precautions, as well as provide safe alternatives for enjoying these foods.
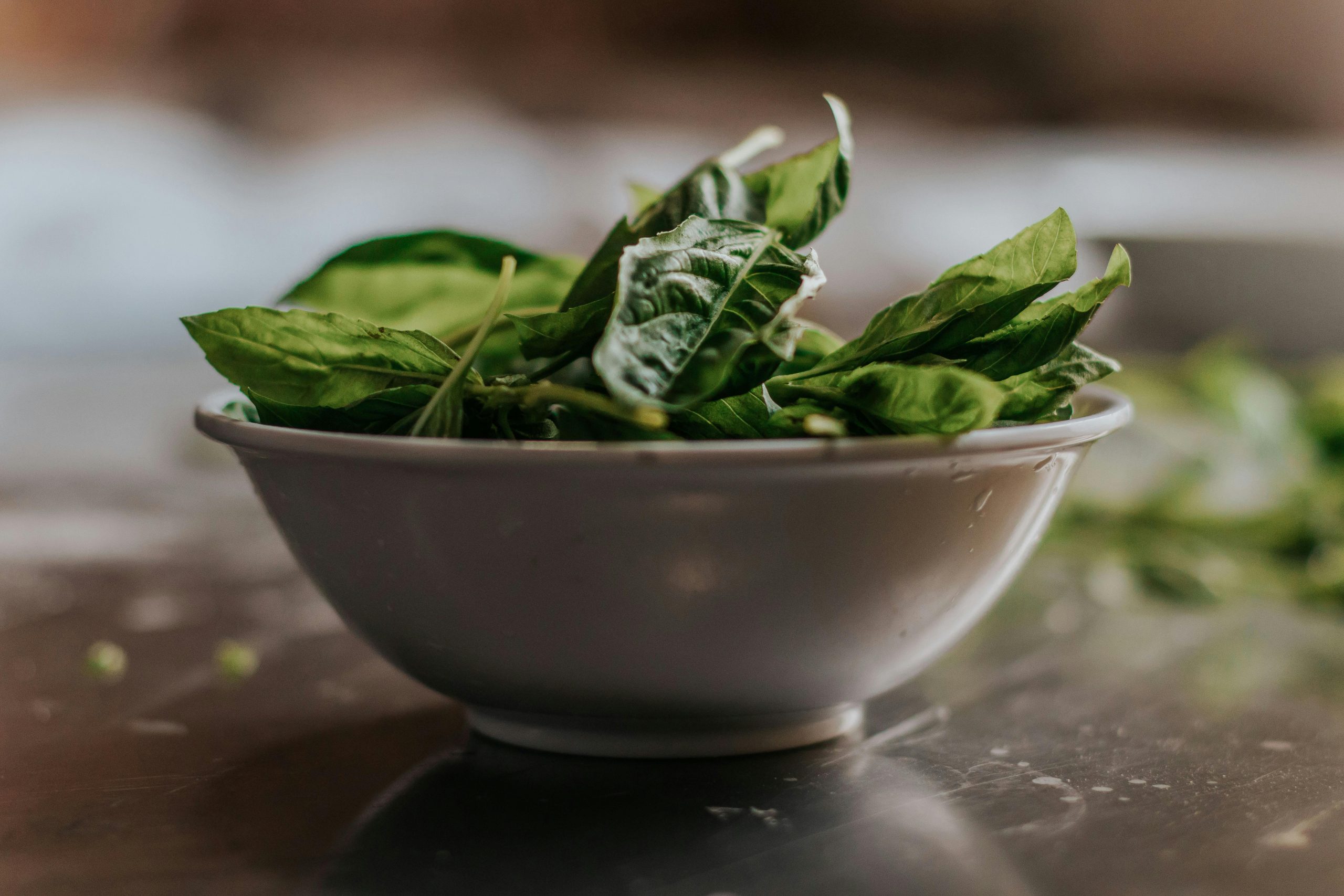

1. Leafy Greens: A Nutritious but Delicate Choice
Leafy greens, including spinach, lettuce, and celery, are often praised for their health benefits. They are loaded with vitamins and minerals essential for well-being, including vitamin K, which is vital for blood clotting, and folate, which supports cellular function and tissue growth. However, reheating these greens can transform their healthy attributes into a potential health hazard. The main culprit lies in the nitrates that are naturally found in these vegetables. When exposed to high temperatures, nitrates can convert into nitrites and then further into nitrosamines—compounds that are associated with an increased risk of cancer.
To enjoy leftover leafy greens safely, consider consuming them cold in salads or wraps. For example, a fresh spinach salad topped with nuts, fruits, and cheese can be both nutritious and delicious. Alternatively, you can incorporate fresh greens into dishes just before serving to retain their nutritional value without the risk of harmful transformations during reheating. This strategy allows you to maintain both the health benefits and the delightful crunch that these greens provide.
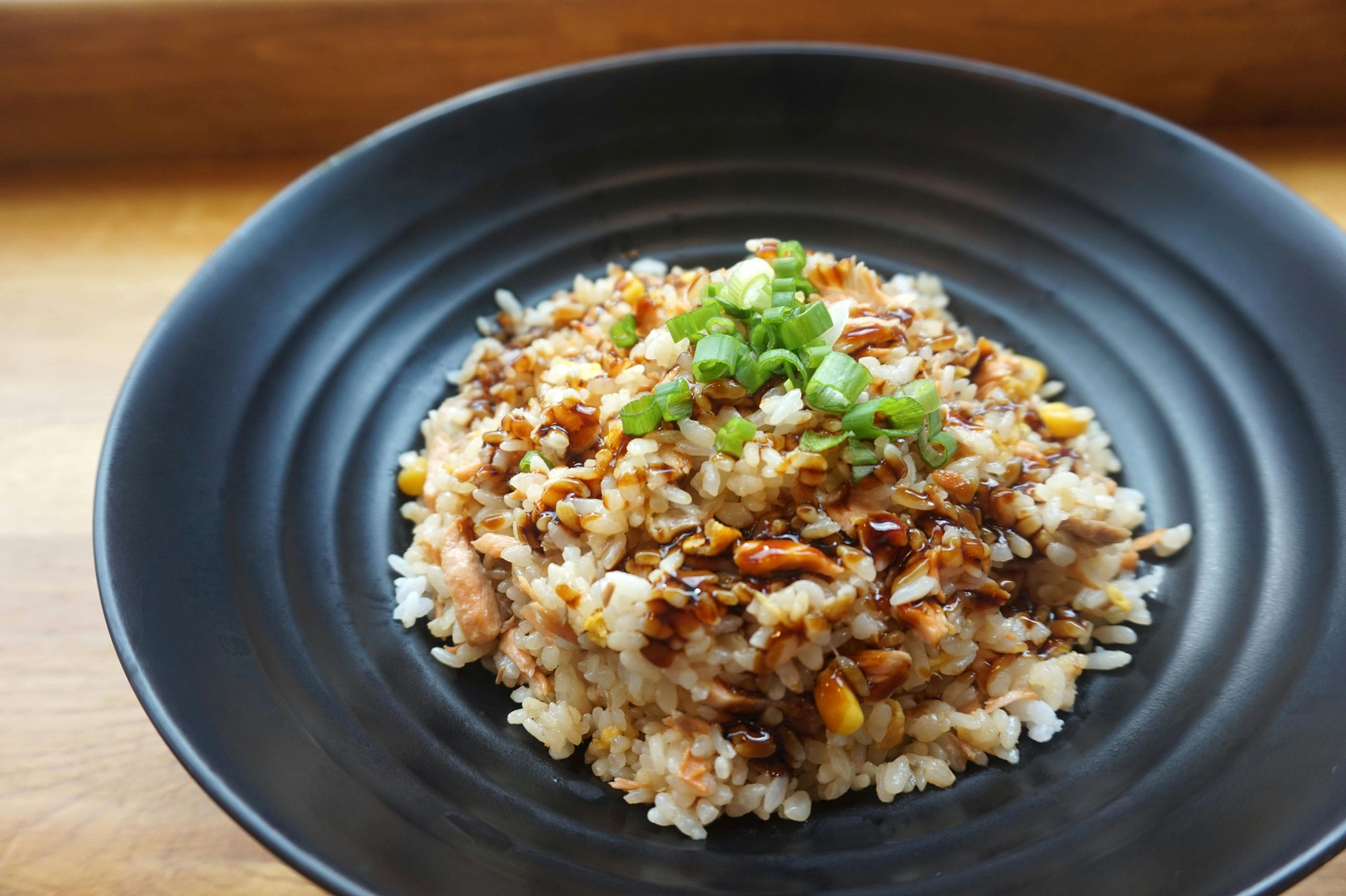

2. The Perils of Reheating Rice
Rice is one of the most common staples worldwide, celebrated for its versatility and ease of preparation. It can serve as a base for countless dishes, from stir-fries to curries. However, reheating rice carries a significant health risk if not managed correctly. Cooked rice can harbor spores of Bacillus cereus, a bacterium that survives cooking and can multiply quickly when the rice is left at room temperature. This bacterium produces toxins that are not destroyed by reheating, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to cool rice promptly after cooking—ideally within an hour—store it in the refrigerator, and reheat it only once until it reaches a steaming hot temperature. For the best safety, consume any leftover rice within a 24-hour period or utilize it immediately in fried rice dishes. If you find yourself with leftover rice, consider using it in a rice salad with vegetables and a light dressing to maintain its flavor while ensuring your health.
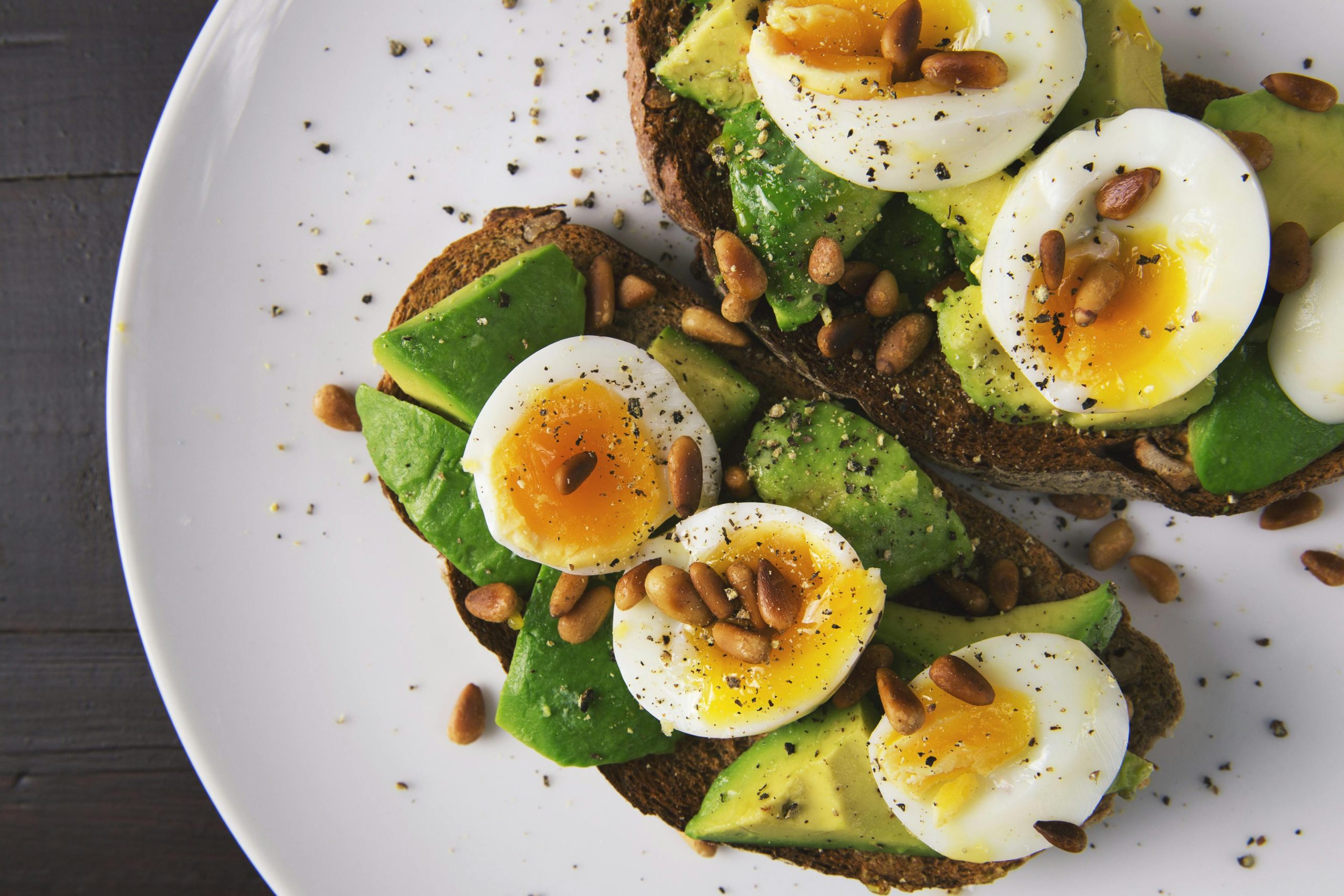

3. Eggs: A Breakfast Favorite with Caution
Eggs are a beloved breakfast staple known for their high protein content and versatility in various dishes, including omelets, scrambles, and frittatas. However, reheating eggs can result in the release of sulfur compounds that may lead to digestive discomfort or worse health issues. Additionally, if eggs are left out for an extended duration, they can become contaminated with bacteria such as Salmonella, which can cause serious gastrointestinal illness.
To safely enjoy leftover eggs, consider consuming them cold, such as in salads or sandwiches, or if reheating is necessary, do so gently and ensure they are cooked thoroughly to minimize health risks. For instance, a cold egg salad can be a refreshing and protein-packed lunch option. If you prefer hot eggs, reheat them lightly on low heat and add fresh herbs or spices to elevate their flavor and appeal.
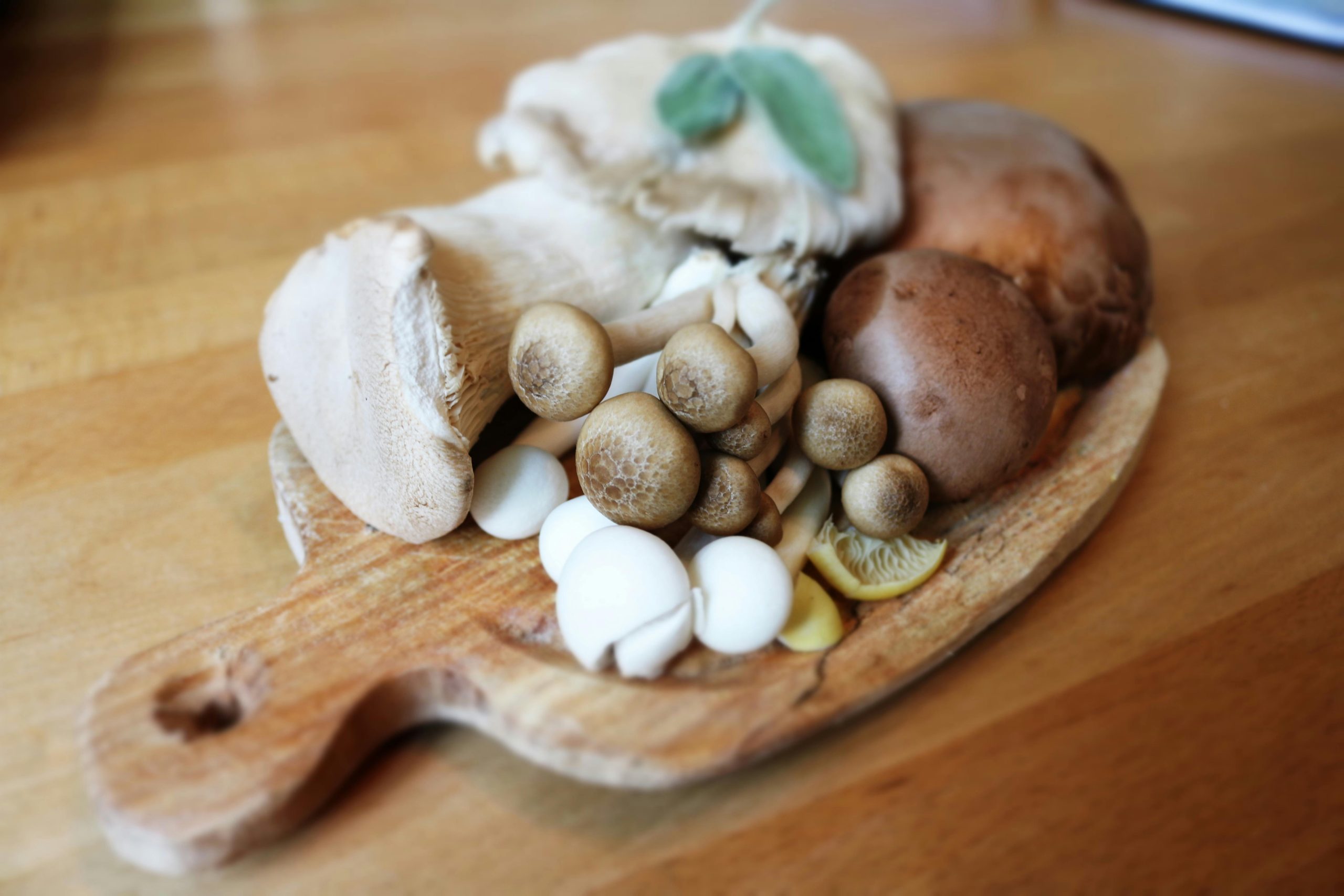

4. The Risks Associated with Mushrooms
Mushrooms are not only a flavorful addition to many dishes, but they also offer a variety of health benefits, including antioxidants and vitamins such as vitamin D. However, mushrooms are particularly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. When reheated, the proteins in mushrooms can break down, creating compounds that may cause gastrointestinal distress and food poisoning. Furthermore, improper storage of mushrooms can facilitate bacterial growth, making them unsafe to eat after a certain period.
To ensure safety, it is best to consume mushrooms shortly after cooking. If you have leftovers, store them properly in the refrigerator and consume them within a day without reheating, or incorporate them into new dishes immediately, such as a savory mushroom risotto or a hearty soup. These options allow you to enjoy the flavor and health benefits of mushrooms while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
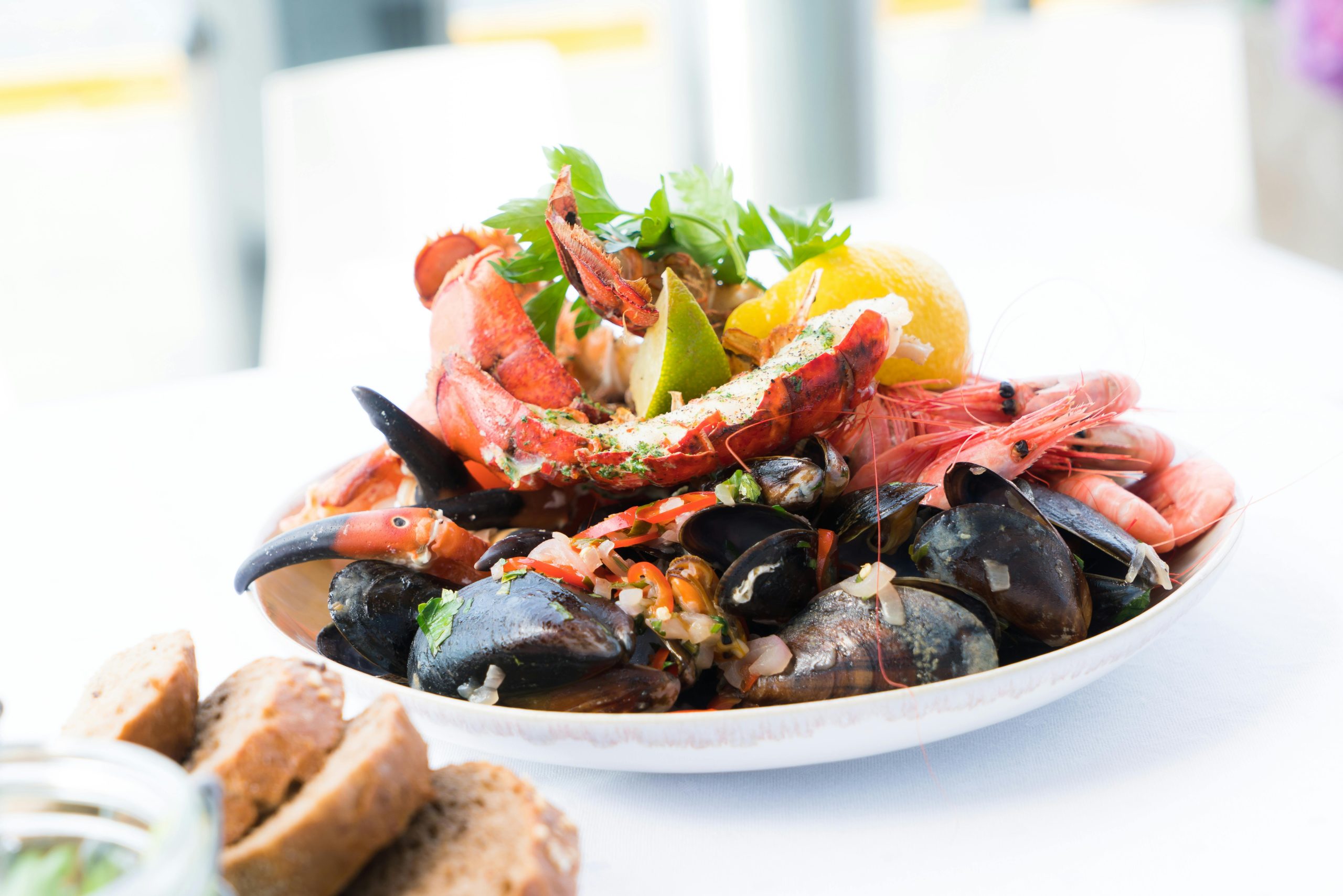

5. Seafood: A Delicate Delight
Seafood is known for its rich flavor and high nutritional content, making it a popular choice for many meals. However, seafood tends to spoil quickly, increasing the risks associated with reheating. Even if cooked seafood appears and smells fine, it may still harbor harmful bacteria or toxins that can lead to foodborne illnesses, such as scombroid or ciguatera poisoning. These toxins are not eliminated through reheating, which poses a significant risk to health.
To maintain the safety of cooked seafood, always refrigerate the leftovers immediately after cooking and aim to consume them within 24 hours. If you do plan to reheat seafood, ensure it is stored correctly and heated thoroughly to reduce any potential risks. For instance, using leftover cooked shrimp in a stir-fry or a seafood pasta dish can be a delicious way to utilize your leftovers while ensuring your safety.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Food Safety
In conclusion, while meal prepping can greatly enhance our daily efficiency and dietary health, awareness of food safety is paramount. Certain foods like leafy greens, rice, eggs, mushrooms, and seafood can pose serious health threats if not handled properly. To ensure a safe and healthy meal prep experience, always prioritize proper cooking, cooling, and reheating methods. By following these guidelines, consumers can enjoy the convenience of meal prep without compromising their health. Remember that food safety is not just about prevention; it’s about making informed choices to protect yourself and your loved ones from potential health risks.