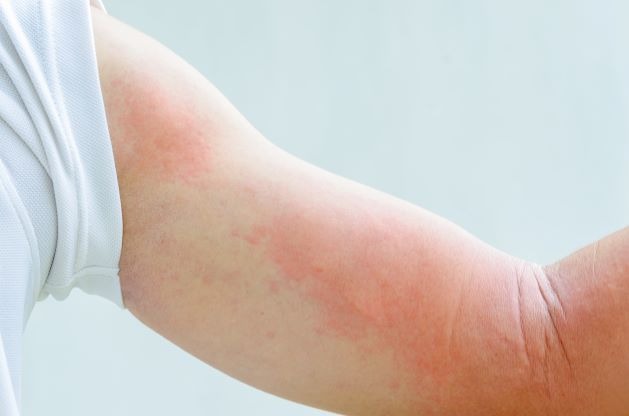
Understanding Hives: A Deep Dive into a Common Skin Condition
The sensation of itchy skin is a common experience that many individuals encounter at various points in their lives. Often, this discomfort stems from relatively benign sources such as a new laundry detergent, dry air, or seasonal allergies. However, when the itching becomes persistent or widespread, it may indicate a more significant health concern, such as chronic hives or urticaria. This article delves into the nature of hives, differentiates them from typical allergies, outlines key symptoms, and discusses recommended management strategies based on medical expertise.
What Are Hives?
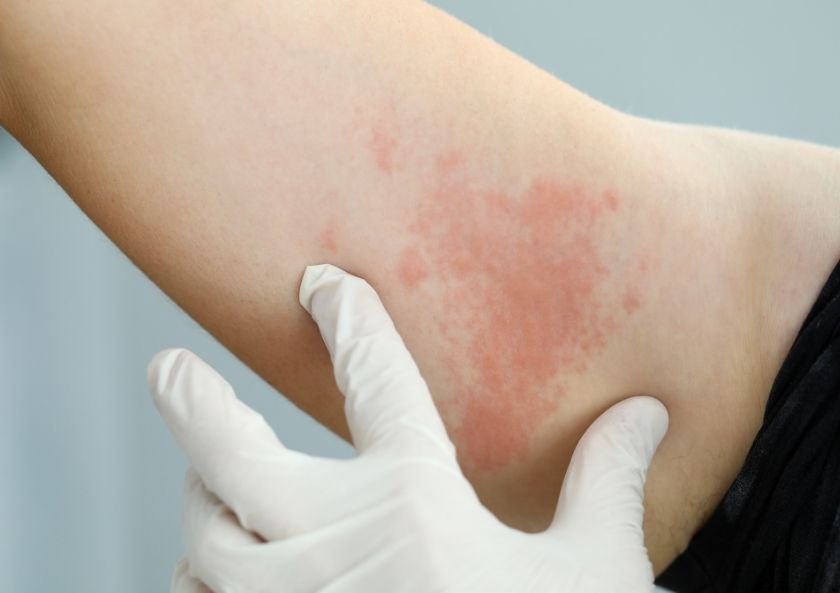
Hives, medically known as urticaria, are characterized by raised, red welts on the skin, often accompanied by intense itching. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) explains that these welts arise when the body releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream, typically following exposure to an allergen or certain triggers. Hives can be categorized into two primary types: acute and chronic. Acute hives appear suddenly and usually resolve within six weeks, often linked to allergens like certain foods or medications. On the other hand, chronic hives persist for over six weeks and may recur intermittently for months or even years, frequently without any identifiable cause.
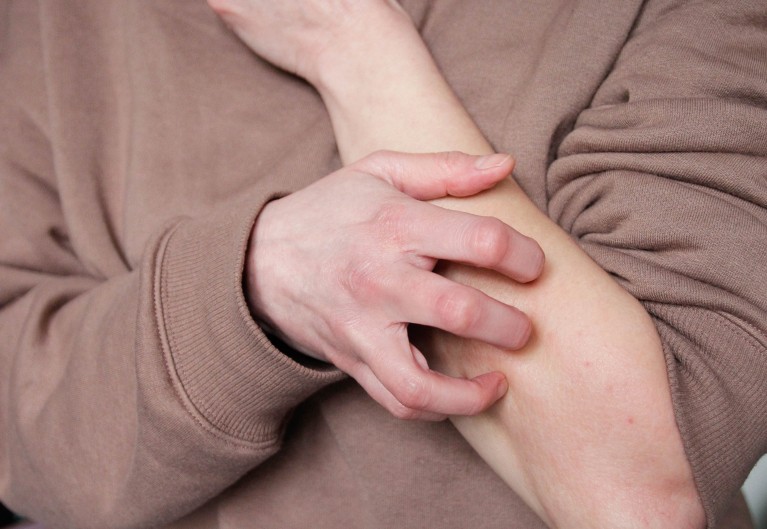
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hives
Understanding the symptoms associated with hives is crucial for prompt recognition and treatment. According to the Mayo Clinic, typical signs of urticaria include:
- Raised, itchy welts that may vary in color, appearing either red or skin-toned.
- Welts that differ in size and shape, sometimes merging to create larger patches.
- Welts that can appear and disappear in different areas of the body.
- Accompanying swelling, known as angioedema, particularly around sensitive regions such as the eyes, lips, or extremities.
- Increased itching that may worsen at night or after physical activities.
In severe cases, hives may be accompanied by alarming symptoms such as dizziness, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
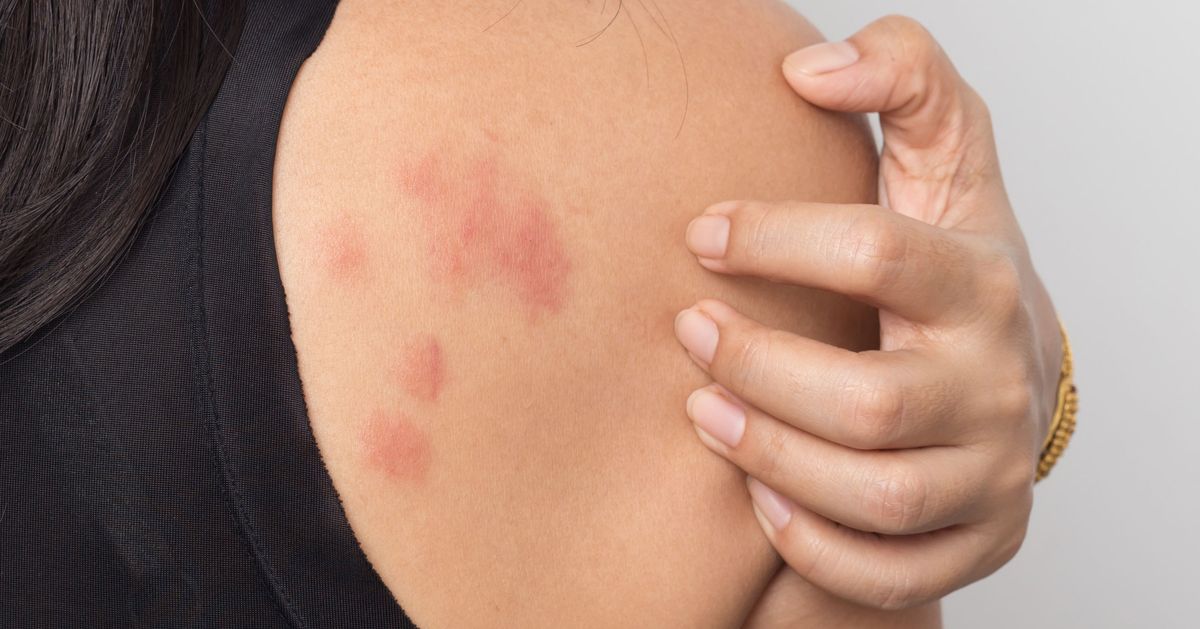
Common Triggers for Hives
Identifying the triggers of hives can be a complex endeavor, as they can arise from a multitude of sources. Common triggers include:
- Food Allergens: Shellfish, nuts, eggs, and specific fruits are frequent culprits.
- Medications: Certain antibiotics like penicillin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provoke hives in sensitive individuals.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollen, animal dander, or insect bites often leads to allergic responses.
- Physical Stimuli: Factors such as pressure, temperature fluctuations, sunlight exposure, or vigorous exercise.
- Infections: Various viral infections, including the common cold or flu, may trigger hives as well.
- Emotional Stress: Psychological triggers can exacerbate symptoms in individuals predisposed to hives.
- Autoimmune Reactions: In chronic cases, the immune system may misidentify healthy skin as a threat.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of hives resolve independently or respond well to over-the-counter antihistamines, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional under certain circumstances. You should seek medical attention if:
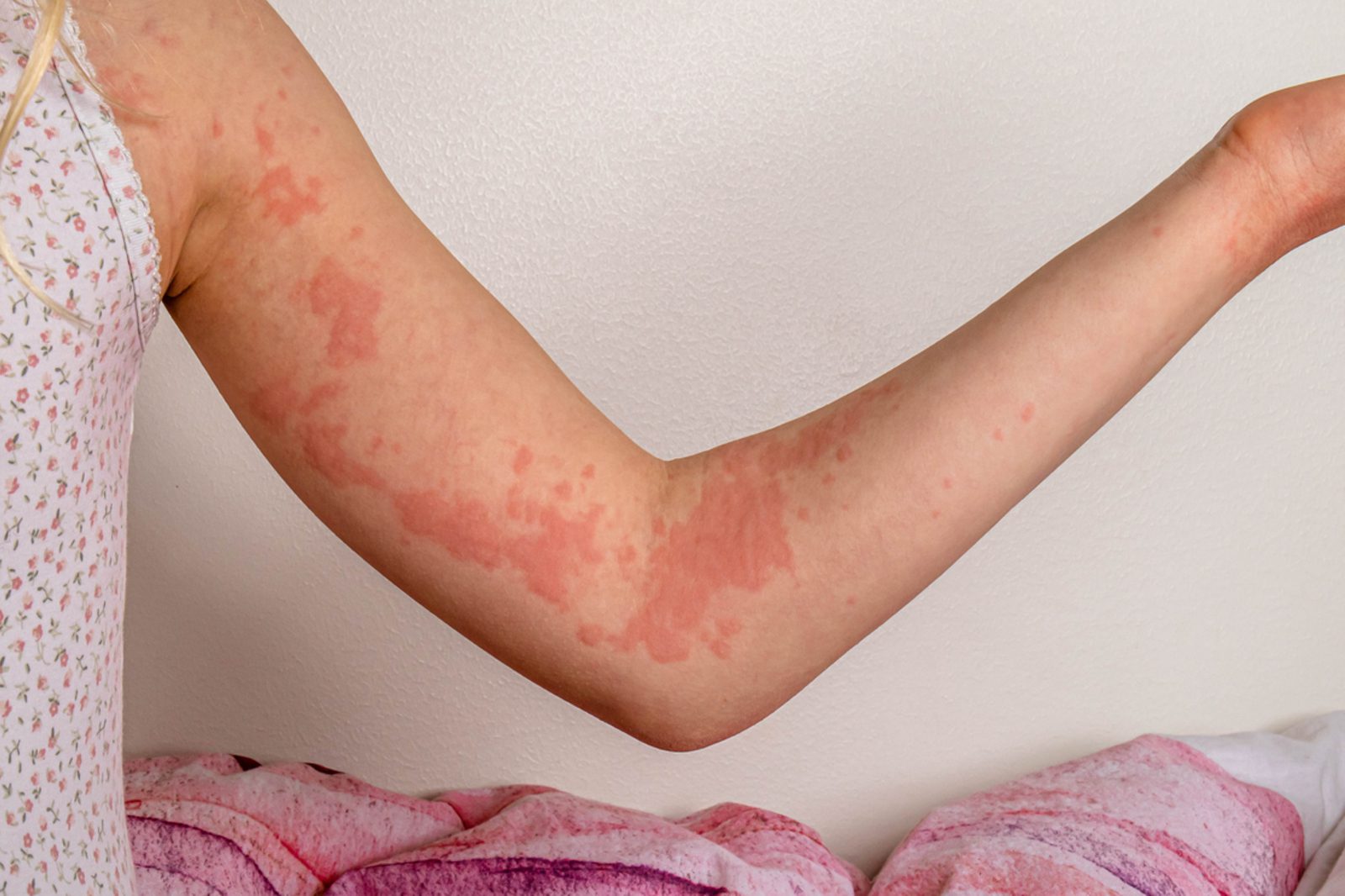
- Your hives persist for more than a few days without improvement.
- You experience recurring episodes without a clear trigger.
- The welts become painful or develop blisters.
- You notice swelling of the face or have difficulty breathing.
A healthcare provider will be able to evaluate your symptoms, rule out serious underlying conditions, and suggest appropriate treatment options.
Effective Treatment Options for Hives
The management of hives typically begins with the use of antihistamines, which act as the first line of defense. Non-drowsy options such as cetirizine or loratadine can help alleviate itching and swelling by blocking histamine release. If standard antihistamines do not provide relief, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications or a combination of treatments, including:

- Hydroxyzine or Diphenhydramine: Often recommended for nighttime use to manage severe symptoms.
- Montelukast: A leukotriene receptor antagonist that may aid in reducing inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Short-term use may be advised for particularly severe flare-ups.
- Omalizumab: An injectable biologic medication specifically designed for chronic urticaria.
Identifying and avoiding known triggers is crucial for preventing future outbreaks. Once triggers are identified through testing, taking measures to steer clear of them can significantly mitigate recurrence.
Home Care and Lifestyle Recommendations
In addition to medical interventions, several home care strategies can help alleviate the discomfort associated with hives. Consider these evidence-based approaches:
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected skin can provide immediate relief.
- Lukewarm Baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths are particularly soothing for irritated skin.
- Fragrance-Free Moisturizers: Keeping your skin well-hydrated with unscented lotions can help reduce sensitivity.
- Loose-Fitting Clothing: Wearing breathable fabrics like cotton can minimize irritation.
- Avoiding Hot Showers: Hot water can exacerbate itching, so opt for lukewarm showers instead.
These recommendations are endorsed by both the AAD and the National Eczema Association, especially for those with sensitive skin.
Debunking Myths About Hives
It is essential to be aware of common myths and misinformation surrounding hives. A few prevalent misconceptions include:
- “Natural Remedies Can Cure Chronic Hives”: While some natural treatments may provide temporary relief, they should never replace proven medical therapies.
- “Itching Always Indicates an Allergy”: Persistent itching can signal other conditions, including liver issues or autoimmune diseases.
- “Hives Are Contagious”: While hives themselves are not contagious, the infections that may trigger them can be.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatments, especially those involving essential oils or herbal products, as they may lead to adverse effects.
Living with Chronic Hives
Chronic hives can lead to significant frustration and discomfort, yet effective management allows individuals to live full and healthy lives. Key strategies include ongoing monitoring of symptoms, avoidance of known triggers, and regular communication with healthcare providers. The AAD indicates that many patients see improvement over time, with some achieving full resolution. Additionally, support groups, both online and in-person, can provide crucial emotional support and effective coping strategies for those affected.
Conclusion
While an itchy sensation may initially seem trivial, persistent or widespread hives warrant careful attention. With a professional diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan incorporating both medical and home-care strategies, hives can be effectively managed. Staying informed and seeking timely assistance is key to safeguarding your skin health and overall well-being.