Why Is Your Fuel Door on the ‘Wrong’ Side?
Have you ever pulled into a gas station, only to find yourself maneuvering awkwardly because your fuel door is on the opposite side? You’re certainly not alone in this peculiar scenario. The position of gas tanks has intrigued car owners and drivers for years. While it may seem like a simple aesthetic choice or a minor oversight, there is a comprehensive rationale behind why fuel doors are situated where they are. This article will explore the engineering, consumer habits, and safety factors that contribute to the diverse placements of gas tanks across various vehicles.

Engineering Constraints and Practical Considerations
The core reason behind the placement of fuel doors can be traced back to engineering practicality. Designing a vehicle is a complex endeavor that requires balancing various factors, including the structure of the underbody and the layout of the fuel system. Steve Yaeger, a spokesperson for Nissan, emphasizes that the location of the fuel door is largely dependent on how the fuel tank is configured and how the filler tube is routed. Various structural components—such as axles, exhaust systems, and suspension parts—often dictate which side can accommodate the necessary fuel lines.

Mark Schirmer from Ford supports this perspective, indicating that automobile manufacturers prioritize seamless integration over symmetry. While it may seem intuitive to design a vehicle with fuel doors on both sides, the logistical challenges and associated costs make this approach impractical in most cases. These considerations create a landscape where the placement of the fuel door is engineered not just for aesthetics but also for functionality.

Regional Preferences and Consumer Habits
Interestingly, the placement of gas tanks varies notably by region. In the United States, the vast majority of cars feature fuel doors on the left side, allowing drivers to fill up without stepping too far from their vehicles. Conversely, in countries like Japan and the UK, fuel doors are typically found on the right side, which aligns with the local driving norms. This discrepancy is rooted in driver habits; American drivers prefer left-side fuel doors, making it easier to access fuel pumps while minimizing the risk of stepping into traffic.

Ford conducted research in the 1980s that confirmed this American preference for left-sided fuel doors. However, this left-side placement has its drawbacks. For instance, it can sometimes lead to car doors colliding with cement pump islands—a design flaw that manufacturers chose to address by reinforcing the doors rather than altering the fuel door’s placement.

Safety Considerations in Fuel Door Design
Safety is another critical factor that has influenced the design and placement of fuel doors. Historically, some automakers opted to place fuel doors on the passenger side, believing this would reduce the risk of fire in the event of a collision on the driver’s side. However, subsequent studies, including research conducted by Ford, revealed no significant safety advantages between driver-side and passenger-side placements. In areas like Germany, where high-speed autobahns lack left-side shoulders, passenger-side fuel doors remain preferred to ensure safer refueling away from fast-moving vehicles.

Improving Gas Station Efficiency
If you’ve ever noticed how gas stations seem to handle traffic seamlessly, even during peak hours, it largely has to do with the variability in fuel door placements. Economist Robert Frank suggests that having fuel doors on both sides of vehicles helps reduce congestion at gas stations. If every car had its fuel door on the same side, one side of the station would be overwhelmed while the other remained idle. By distributing fuel doors across both sides, gas stations can better balance traffic flow, thus minimizing wait times for drivers.

A Historical Perspective on Fuel Door Placement
The evolution of fuel door placement is not a recent phenomenon. Back in the 1970s, automakers like Ford commonly positioned fuel doors on the passenger side. This decision stemmed from safety concerns and the desire to protect drivers during refueling. As automotive designs have progressed, so too have placement strategies, as manufacturers now work to balance consumer preferences, regional norms, and engineering requirements. This has resulted in the varied fuel door placements we see in modern vehicles today.
Design Challenges and Finality of Placement
One significant reason for the wide variation in fuel door placements is the difficulty of changing it once a vehicle’s design is finalized. Bharat Balasubramanian, a former executive at Mercedes-Benz, explains that the decision regarding gas tank placement is typically made early in the design process, making late changes challenging. Shifting the fuel door could disrupt the vehicle’s overall structure and functionality, emphasizing the importance of meticulous planning during the initial design phases. Automotive engineers must consider a host of factors, from aerodynamics to crash safety, when determining the optimal location for fuel tank access.
Practical Tips for Drivers
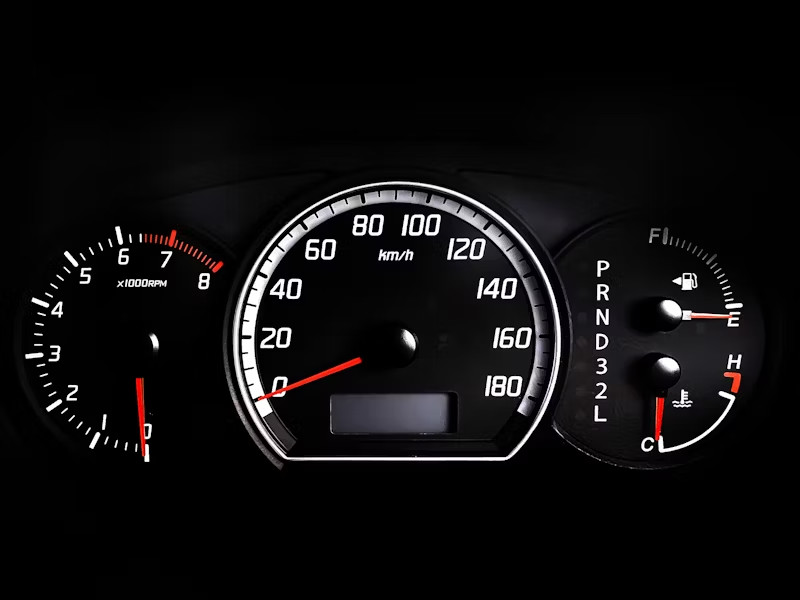
If you find yourself frequently forgetting which side your fuel tank is located on, there’s a straightforward trick to help you remember. Most vehicles come equipped with a small arrow next to the fuel gauge on the dashboard, pointing to the side of the vehicle where your fuel door is situated. This seemingly minor detail has helped countless drivers avoid the awkwardness of pulling up to the wrong side of the pump. Keep this in mind the next time you are unsure about where to fill up!
The Future: Will Electric Vehicles Change Fuel Door Dynamics?
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction in the automotive market, the conversation surrounding fuel door placement may become increasingly irrelevant. Since EVs do not require traditional fuel doors, they present similar but distinct challenges concerning the placement of charging ports. Automakers are experimenting with various port locations, ranging from the front grille to the rear quarter panel, all while aiming to combine convenience with functionality. Although the design considerations differ, the fundamental principles of engineering, safety, and consumer preferences remain crucial in determining the optimal configuration.
For more insights into why fuel doors are located on different sides of vehicles, you can explore this article on AutoTrader.