The Evolution of Airport Security: Balancing Safety and Privacy
In the wake of rising global security threats, the landscape of airport security has undergone significant transformation over the past two decades. Among the most controversial innovations were the full-body scanners, which came to symbolize a contentious intersection between enhanced safety measures and personal privacy. Dubbed by critics as “virtual strip searches,” these machines ignited fierce debate among travelers, civil liberties advocates, and security agencies alike. This article delves into the history, implications, and eventual evolution of airport body scanners, shedding light on the delicate balance between security and privacy.
Historical Context: The Rise of Body Scanners
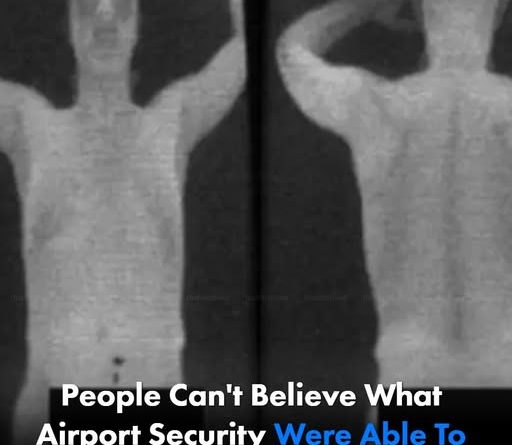
The introduction of full-body scanners began in earnest after the failed Christmas Day bombing attempt in 2009, which exposed significant vulnerabilities in airport security protocols. In response, the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) accelerated the implementation of advanced imaging technology. Among these innovations were the controversial backscatter X-ray scanners, developed by companies like Rapiscan. These devices were engineered to detect nonmetallic threats, such as explosives, hidden beneath clothing—an advancement deemed necessary in an era marked by escalating terror threats.
The timing of this technological shift was critical; following the September 11 attacks, airport security had already been heightened dramatically. However, the Christmas Day incident revealed that despite these measures, there were still gaps that could be exploited by those intent on causing harm. The TSA’s response was to adopt measures that were not only reactive but also preventative, implementing body scanners as a way to deter potential attacks before they could occur.
The Reaction: Public Outcry and Privacy Concerns
Despite their intended safety benefits, body scanners quickly faced backlash from the public. Many travelers reported feelings of discomfort and vulnerability as they underwent what felt like a highly invasive procedure. The scanning process involved specific poses and strict positioning, with passengers often instructed to stand still, arms raised above their heads, while they were subjected to scrutiny behind opaque glass. The stark realization that these machines produced highly detailed images of their bodies led to widespread anxiety about privacy violations.
Moreover, numerous advocacy groups and civil liberties organizations began to voice their concerns. For instance, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) firmly opposed the use of body scanners, arguing that they violated the Fourth Amendment rights against unreasonable searches. This opposition stemmed from the belief that airport security protocols should never come at the expense of individuals’ rights to privacy. High-profile figures and celebrities joined the conversation, further amplifying the debate surrounding the ethics of scanning technologies.
The Technology: From Backscatter to Millimeter Wave Scanners
As the controversy intensified, privacy advocates raised valid concerns regarding the ethical implications of such intrusive technology. Critics argued that the images produced by backscatter scanners were not only unnecessary for ensuring safety but also posed a significant threat to personal dignity. Anonymity was moot when the scans laid bare intimate anatomical details. In light of public outcry and mounting pressure, by 2013, the TSA shifted to a more privacy-conscious approach. This led to the introduction of Automated Target Recognition (ATR) software, which replaced explicit body images with generic outlines, effectively addressing many of the privacy concerns that had surfaced.
The transition to millimeter wave scanners represented a paradigm shift in airport security. Instead of showing detailed images of passengers, these newer scanners use non-ionizing radio waves to detect potential threats while preserving the anonymity of travelers. This change was instrumental in demonstrating that effective security measures could exist without infringing on personal privacy. Additionally, the new technology was met with more public acceptance, partly because it aligned better with the growing societal demand for privacy protections.