The Vital Role of Magnesium in Human Health
Magnesium is a crucial mineral that plays an instrumental role in the human body, involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions. This essential mineral is vital for maintaining optimal health across various systems, influencing everything from muscle contraction and nerve function to bone integrity and the immune response. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of magnesium, focusing on its potential in alleviating bone pain, managing diabetes, reducing anxiety and depression, and alleviating digestive issues like constipation. Moreover, we will explore effective ways to incorporate magnesium into your health regimen for maximum benefits, emphasizing the importance of this mineral in everyday life.

1. Magnesium and Bone Health
Magnesium is pivotal in the process of bone mineralization. It aids in regulating the levels of calcium in the body, which is essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to diminished bone density, increasing the likelihood of fractures and chronic bone pain. Research studies suggest that adequate magnesium intake can help prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. In fact, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research indicates that individuals with higher magnesium intake tend to exhibit greater bone density compared to those with lower intakes.
How to Use Magnesium for Bone Health
Recommended Forms: Magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are often recommended for their superior absorption rates. These forms are better utilized by the body compared to others, making them excellent choices for those looking to improve their bone health.

Dosage: For adults, a daily intake of 300 to 400 mg is typically advised. To enhance absorption, it’s recommended to take magnesium supplements alongside vitamin D and calcium, as these nutrients work synergistically to support bone health.
Dietary Tips: Incorporate magnesium-rich foods into your diet. Excellent choices include leafy greens like spinach and Swiss chard, nuts such as almonds and cashews, and seeds like pumpkin and sunflower seeds. It’s important to note that excessive calcium intake without adequate magnesium may lead to calcium deposits in soft tissues, which can be detrimental to overall health.
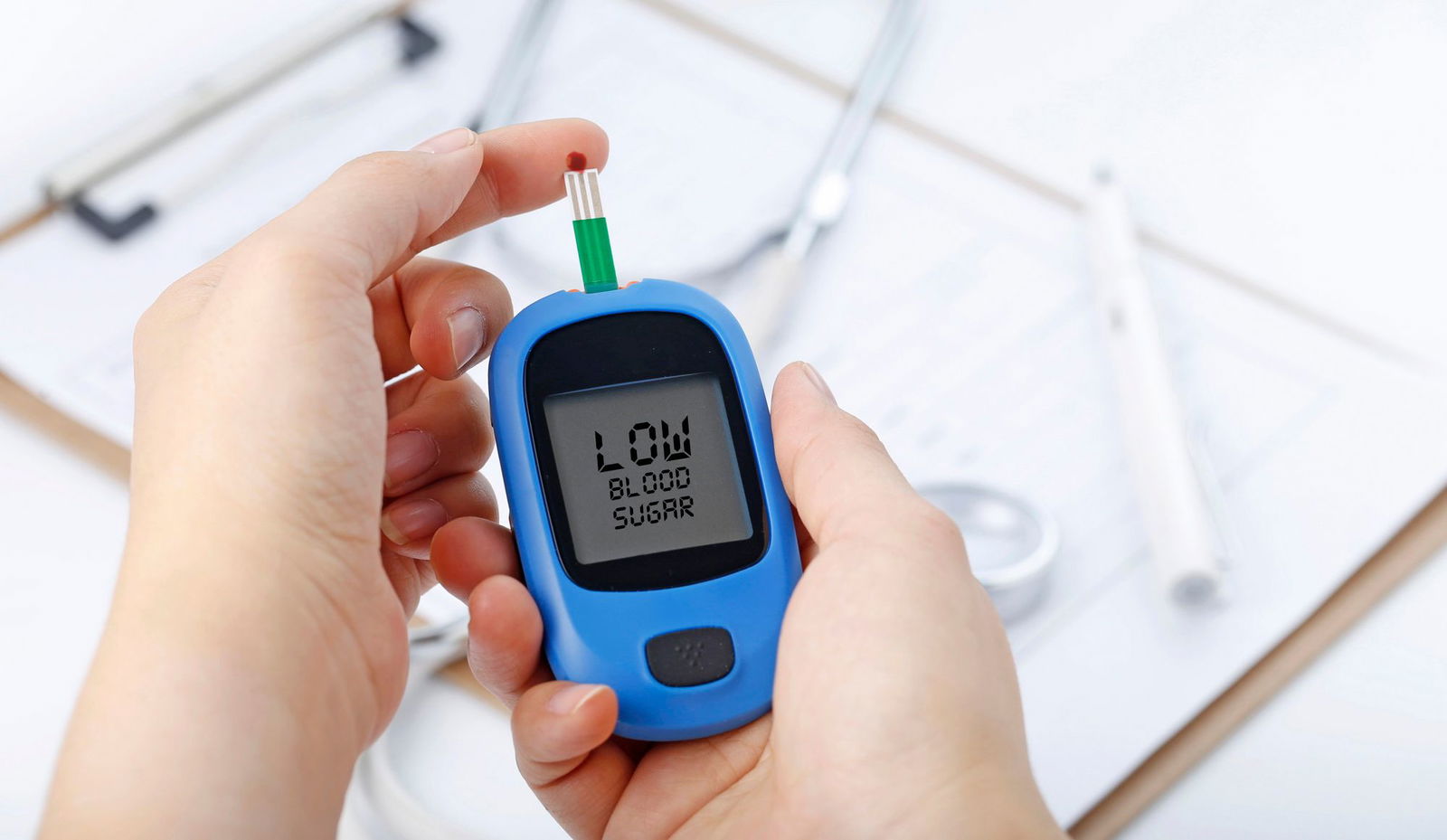
2. Magnesium in Diabetes Management
Emerging research highlights magnesium’s role in glucose metabolism and its potential to enhance insulin sensitivity. Studies have shown a correlation between low magnesium levels and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake can be a proactive step in diabetes management. For instance, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that those who consumed higher amounts of magnesium had a significantly reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
How to Use Magnesium for Diabetes
Recommended Forms: Magnesium chloride and magnesium taurate are beneficial; taurine, present in magnesium taurate, also supports insulin regulation. These forms can improve glucose control and enhance overall metabolic function.
Dosage: A daily intake of 250 to 350 mg is generally sufficient, ideally taken after meals to minimize post-meal glucose spikes. Timing is key, as this can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Dietary Tips: Incorporating whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, beans such as lentils and black beans, and even dark chocolate can help boost magnesium levels while providing additional health benefits. However, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider if you are on medications for blood sugar control to avoid the risk of hypoglycemia.
3. Magnesium’s Role in Mental Health
Magnesium is increasingly recognized for its role in mental well-being. It helps regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA, which are essential for mood stabilization. Insufficient magnesium levels have been linked to increased stress, irritability, and a higher prevalence of clinical depression. In fact, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Affective Disorders suggests that individuals with lower magnesium levels tend to report higher levels of anxiety and depressive symptoms.
How to Use Magnesium for Mental Health
Recommended Forms: Magnesium threonate is particularly effective as it crosses the blood-brain barrier, making it a potent option for cognitive health. This specific form of magnesium has shown promise in studies relating to memory and learning enhancement.
Dosage: A daily dose of 200 to 400 mg is advised, preferably taken in the evening to aid relaxation and improve sleep quality, as good sleep is vital for mental health.
Lifestyle Tips: To further enhance the calming effects of magnesium, consider combining its intake with mindfulness techniques or deep breathing exercises. Practicing yoga or meditation can also complement magnesium’s benefits. Additionally, it’s advisable to limit caffeine and alcohol consumption, as these can deplete magnesium levels significantly, thereby undermining any potential benefits.
4. Alleviating Constipation with Magnesium
Magnesium serves as a natural laxative, working by drawing water into the intestines to soften stools and promote bowel movements. Additionally, it helps relax the muscles of the digestive tract, making it an effective remedy for constipation. Several studies have indicated that magnesium supplementation can significantly improve bowel regularity.
How to Use Magnesium for Digestive Health
Recommended Forms: Magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate are commonly used to alleviate constipation. Magnesium citrate is often preferred due to its higher bioavailability and effectiveness in promoting bowel movements.
Dosage: A dosage of 400 to 500 mg at night is often effective, but starting with a smaller dose to assess tolerance is recommended. It’s crucial to note that magnesium laxatives should not be used continuously for more than a few days without medical supervision, as prolonged use can lead to dependency.
Dietary Tips: Staying well-hydrated and consuming fiber-rich foods, such as oats, vegetables, and prunes, can enhance digestive health and prevent constipation. Additionally, incorporating probiotics through fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi can support a healthy gut microbiome, further aiding digestion.
Identifying Magnesium Deficiency
Common signs of magnesium deficiency include:
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Fatigue or low energy
- Frequent headaches or migraines
- Insomnia
- Tingling or numbness
- Anxiety or mood swings
- Irregular heartbeat
If you identify multiple symptoms, a simple blood test can help confirm low magnesium levels. It’s important to monitor your magnesium intake, particularly if you’re experiencing these symptoms, as they can significantly impact your quality of life.
Precautions and Final Recommendations
When considering magnesium supplements, always opt for high-quality products that are free from unnecessary fillers and additives. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation is essential, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or taking other medications. Overconsumption of magnesium, particularly through supplements, can lead to side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. Therefore, it’s crucial to approach supplementation wisely and under professional guidance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnesium is a powerhouse mineral that contributes significantly to various aspects of health. By simply incorporating magnesium into your daily regimen—whether through dietary sources or carefully chosen supplements—you can enhance your bone health, regulate blood sugar, improve your mood, mitigate anxiety, and promote healthier digestion. The benefits of magnesium are far-reaching and can profoundly impact your overall well-being and quality of life. Emphasizing the importance of this mineral can lead to better health outcomes and a more fulfilling life.

















