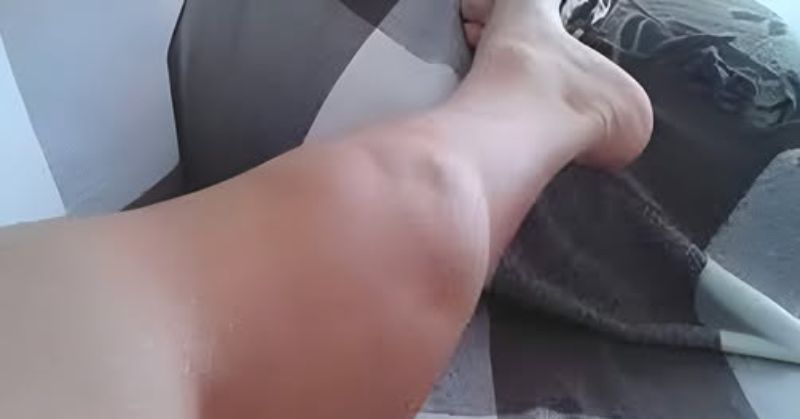
Understanding Night Cramps: Who is at Risk and Why
Night cramps, characterized by unexpected and painful muscle contractions that typically occur during sleep, are a widespread issue affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. This phenomenon can disrupt peaceful slumber, leading to significant discomfort and distress. While night cramps can potentially affect anyone, certain demographics are notably more susceptible. Understanding the risk factors associated with night cramps is essential for effective prevention and management strategies.
1. Older Adults: A Primary Demographic
Age is a significant factor in the prevalence of night cramps, with research indicating that approximately one-third of individuals over the age of 60 experience these painful episodes regularly. As we age, our bodies undergo a series of physiological changes that make us more vulnerable to these muscle spasms. For instance, there is a natural decline in muscle flexibility and elasticity, which can be exacerbated by reduced physical activity levels common in older adults. Additionally, nerve function, which plays a critical role in muscle control, tends to diminish, affecting how efficiently signals are transmitted to muscles.
2. Pregnant Women: Unique Challenges
Pregnancy introduces a host of physiological changes that can lead to an increased incidence of night cramps, particularly during the second and third trimesters. Although the specific reasons for these cramps are not fully understood, several contributing factors have been identified. The added weight that expectant mothers carry places additional strain on leg muscles and veins, making them more susceptible to cramps. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can disrupt the body’s handling of fluids and essential electrolytes, leading to imbalances in critical minerals such as magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
Furthermore, altered blood circulation patterns during pregnancy may exacerbate the likelihood of muscle cramps. As the growing uterus exerts pressure on blood vessels, the flow of blood to the legs can become restricted, contributing to nighttime cramping. For many women, these cramps can become a frustrating aspect of nightly rest, interrupting sleep and leading to fatigue during the day. To alleviate these symptoms, healthcare providers often suggest maintaining proper hydration, engaging in regular, gentle physical activity, and ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients to support muscle health.3. Athletes and Those Engaging in Physical Activities
Interestingly, individuals who are typically in excellent physical shape, such as athletes, can also find themselves at risk for experiencing night cramps. High levels of physical exertion, whether through rigorous training, extended exercise sessions, or competitive sports, can leave muscles fatigued and dehydrated. When the body loses fluids and essential electrolytes through sweat, the likelihood of cramping significantly increases. Athletes who do not allow for adequate recovery time or fail to engage in proper stretching routines may wake in the night with painful calf or foot cramps, serving as a stark reminder of their physical exertions.
Additionally, the type of exercise performed matters. High-intensity workouts, especially those that involve repetitive movements, can lead to localized muscle fatigue, making specific muscle groups more susceptible to cramping. To combat this issue, athletes are encouraged to prioritize hydration, electrolyte replenishment, and structured cool-down periods following intense physical activity. Incorporating yoga or stretching into their routine can also enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of cramps during rest.4. The Sedentary Lifestyle: An Unexpected Factor
Conversely, individuals leading sedentary lifestyles are also vulnerable to experiencing night cramps, albeit for different reasons. Prolonged periods of sitting or standing can impede blood circulation in the legs, leading to muscle stiffness that may manifest as cramps during rest. Those in office environments, retail positions, or jobs requiring extended periods of inactivity frequently report experiencing these uncomfortable nighttime episodes.
The absence of regular movement or stretching throughout the day can exacerbate the problem, highlighting the need for incorporating physical activity into daily routines. Simple strategies, such as taking brief breaks to stand, stretch, or walk around, can significantly improve circulation and muscle function. Additionally, ergonomic adjustments in the workplace, such as using standing desks or employing proper posture, can help alleviate pressure on muscles and reduce the risk of cramps during sleep.5. Underlying Health Conditions: A Compounding Risk
Certain medical conditions can significantly elevate the risk of night cramps, warranting special attention. Individuals with diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or other circulation-related issues often experience cramps due to limited blood flow. Neurological disorders that affect nerve communication with muscles may also trigger spasms. Furthermore, thyroid imbalances or chronic kidney disease can disrupt electrolyte levels in the body, contributing to the occurrence of cramps.
In many cases, these cramps are not isolated incidents but rather indicators of more significant underlying health issues that necessitate medical evaluation and intervention. For example, diabetic neuropathy can lead to irregular signals sent to muscles, promoting involuntary contractions. Understanding the connection between these health conditions and night cramps can empower individuals to seek appropriate medical advice and treatment, ultimately improving their quality of life and sleep.6. The Role of Medications: A Cautionary Note
Finally, medications play a substantial role in the incidence of night cramps, serving as a cautionary note for many individuals. Diuretics, commonly prescribed to manage high blood pressure, can lead to increased fluid loss and subsequent electrolyte imbalances. Certain cholesterol-lowering medications, birth control pills, and even some asthma treatments have also been associated with muscle cramping. If a person notices a pattern of cramps following the initiation of a new medication, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional rather than dismissing these symptoms as a normal part of aging or life. By discussing these concerns openly, patients can work with their doctors to explore alternative treatment options or implement strategies to mitigate medication-related side effects. This proactive approach can significantly enhance overall well-being and improve sleep quality.In conclusion, night cramps represent a common yet often underestimated issue that can disrupt sleep and affect daily life. By understanding the various risk factors—including age, pregnancy, physical activity levels, underlying health conditions, and the influence of medications—individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their occurrence. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, better hydration practices, or seeking medical advice, addressing the root causes of night cramps can lead to improved sleep quality and overall well-being, allowing individuals to enjoy restful nights and rejuvenated days.