Why Up to 80% of People May Have a Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is one of the most important minerals for our body, playing a crucial role in hundreds of biological functions. From supporting muscle and nerve function to regulating blood sugar levels and maintaining heart health, magnesium is essential for overall wellness. However, recent research suggests that up to 80% of people worldwide may be suffering from magnesium deficiency. So, what’s causing this widespread issue, and how can you tell if you’re affected?
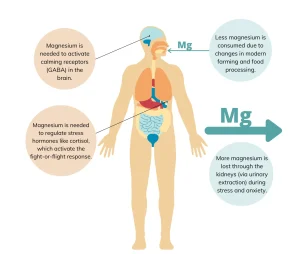
The Importance of Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including protein synthesis, blood pressure regulation, and bone health. It’s also crucial for energy production, helping cells generate the energy they need to function. Without enough magnesium, our bodies can experience a range of symptoms, some of which are easy to ignore or overlook.
Why So Many Are Deficient
One of the main reasons for such a high prevalence of magnesium deficiency is that many people simply don’t get enough magnesium through their diet. Magnesium-rich foods include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains. However, with modern diets often relying heavily on processed foods and refined grains, many people aren’t consuming enough of these magnesium-rich options.
In addition, the soil in which our food is grown has become increasingly depleted of magnesium due to modern farming techniques. This means that even if you are eating a diet rich in vegetables and grains, the magnesium content in your food may not be as high as it once was.

Common Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can vary widely, and some may be subtle enough to go unnoticed for years. Common signs include muscle cramps, fatigue, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and poor bone health. More severe magnesium deficiencies can lead to heart arrhythmias, high blood pressure, and even an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Risk Factors for Deficiency
Certain factors can put you at a higher risk for magnesium deficiency. People with digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, which affect the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, may be more prone to low magnesium levels. Additionally, individuals with high alcohol consumption, those on certain medications, and those who are elderly are at a greater risk of deficiency.
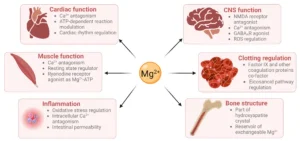
How to Boost Your Magnesium Intake
If you’re concerned about magnesium deficiency, there are several ways to improve your intake. Start by adding more magnesium-rich foods to your diet, such as spinach, almonds, avocados, and black beans. In some cases, magnesium supplements may be recommended, especially for those with higher deficiency levels or specific health conditions. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a role in almost every bodily function, yet many people are unaware that they may be lacking in this essential nutrient. With up to 80% of the population potentially experiencing magnesium deficiency, it’s important to pay attention to your diet and health to ensure you’re getting enough. By making small dietary changes or considering supplementation, you can help ensure your body has the magnesium it needs to thrive.