The Hidden Impact of HPV on Men’s Health
In recent years, health authorities and researchers have increasingly highlighted the significance of understanding human papillomavirus (HPV), an infection that affects millions globally. While much of the discourse tends to focus on women, it is crucial to recognize that men are equally affected by HPV and its associated health risks. The persistent misconception that HPV is primarily a women’s health issue has perpetuated stigma and misinformation, leading to a lack of knowledge and awareness among men. This article aims to shed light on the implications of HPV for men, the ways it spreads, the associated health risks, and the proactive measures that can be taken to mitigate these risks.
Understanding HPV: A Closer Look
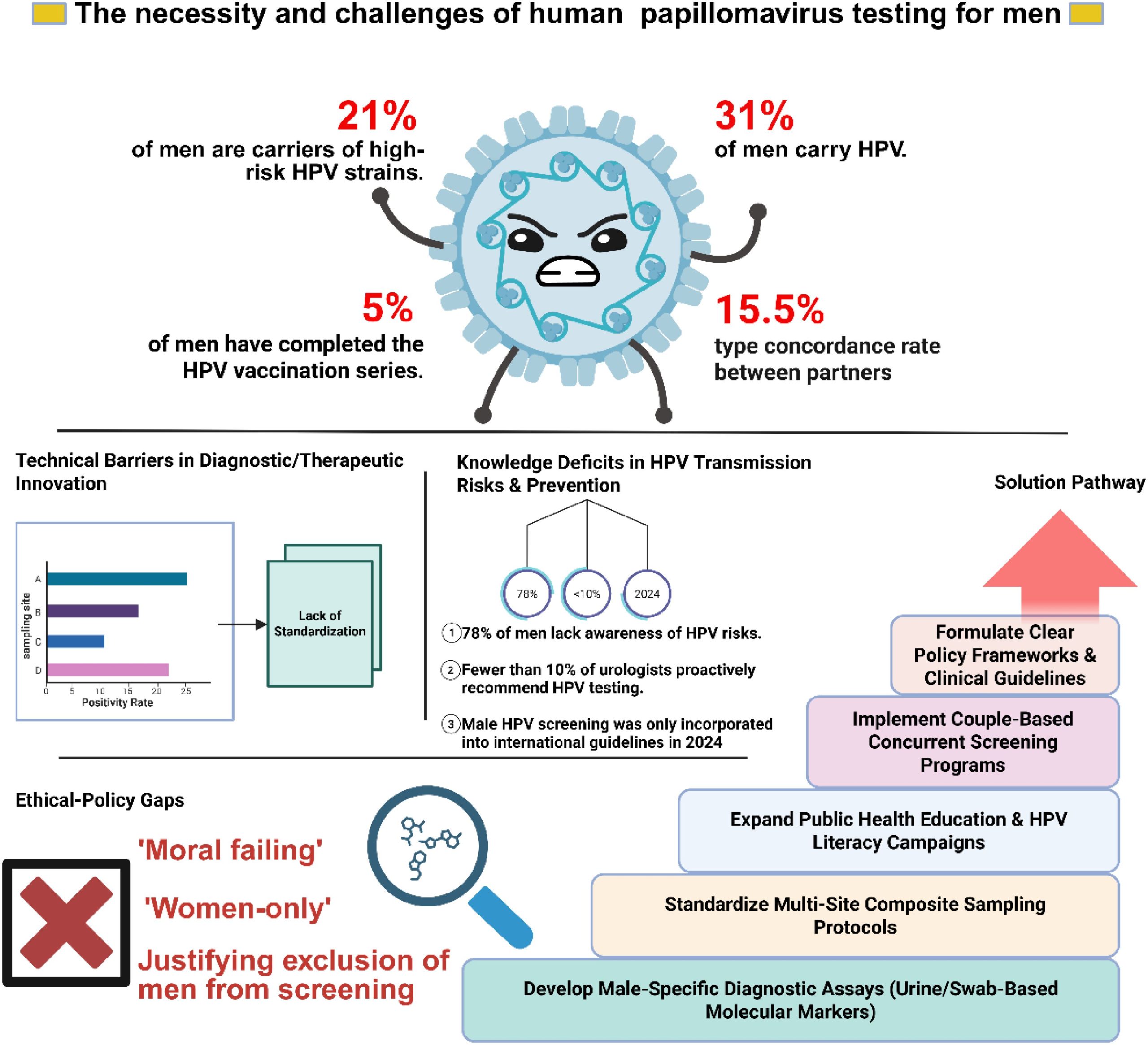
HPV encompasses a group of over 200 related viruses. Among these, some types are categorized as low-risk, causing harmless skin warts, while others are deemed high-risk, as they can lead to various cancers, including cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly all sexually active individuals will contract HPV at some point in their lives. Although the immune system often clears most infections naturally within a couple of years, persistent infections with high-risk strains can pose significant health threats.
Why Men Should Care About HPV
For men, the presence of HPV is associated with several health concerns. High-risk strains of HPV have been linked to serious conditions such as:
- Oropharyngeal cancers, which can arise in the throat, tongue, and tonsils.
- Anal cancers, which are less common but have seen increasing incidence rates.
- Respiratory papillomatosis, a rare condition characterized by benign tumors in the airways.
The widespread nature of HPV makes it a significant public health concern. As men are often unaware of their risk or status, it becomes essential to foster conversations around HPV that include men. By expanding awareness, we not only address personal health but also contribute to community health strategies aimed at reducing HPV transmission.
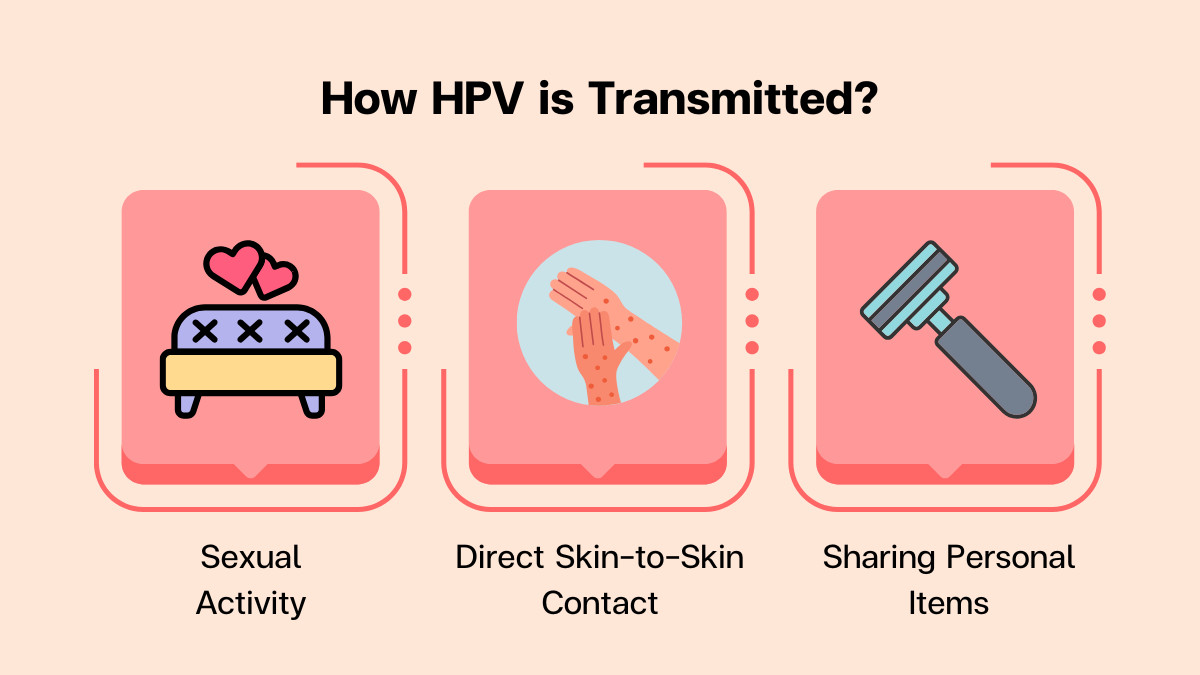
The Mechanism of HPV Transmission
HPV is notably prevalent among the sexually active population due to its ease of transmission. The virus spreads primarily through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activities, and it does not require the exchange of bodily fluids, making it distinct from many other sexually transmitted infections. This silent transmission can occur even when an individual shows no visible signs or symptoms, complicating prevention efforts. As a result, many individuals may not discover their HPV status until complications arise years later.
Risk Factors and Lifestyle Connections
Research indicates that certain lifestyle choices can increase the likelihood of HPV exposure. Individuals with multiple sexual partners are statistically more prone to encountering someone infected with high-risk strains. A study published in the journal Sexually Transmitted Diseases highlights a direct correlation between the number of sexual partners and increased chances of HPV exposure. However, it is vital to note that even a single sexual encounter can result in exposure, emphasizing the need for vigilance regardless of lifestyle.
Recognizing Symptoms and Long-Term Health Risks
HPV infections are frequently asymptomatic, which is why ongoing health awareness is paramount. When symptoms do manifest, they may include:
- Small growths or warts in sensitive areas, which may go unnoticed.
- Respiratory papillomatosis, causing breathing difficulties due to growths in the airways.
- Potential development of oropharyngeal cancers, which can have serious health implications.
While the majority of HPV infections do not progress to severe health conditions, the potential for high-risk strains to cause significant disease underscores the importance of prevention, regular health screenings, and ongoing education. Men must be proactive in understanding the risks associated with HPV to manage their health effectively.
Emotional Implications and the Importance of Awareness
Beyond the physical ramifications, being diagnosed with HPV can have profound emotional consequences. Many men experience feelings of anxiety, confusion, or shame due to the social stigma surrounding sexually transmitted infections. It is essential to foster an environment where open discussions about HPV are normalized, as this can mitigate feelings of isolation and fear. Awareness can help:
- Reduce stigma: Recognizing that HPV is common can alleviate feelings of shame.
- Encourage openness: Discussing health matters with partners fosters trust and shared responsibility.
- Support mental health: Providing education and access to counseling can aid individuals in coping with the diagnosis constructively.
Preventive Measures: A Call to Action
Men can take various proactive steps to minimize their risk of HPV exposure and its potential consequences:
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine, such as Gardasil 9, is the most effective preventive measure. It protects against the most common high-risk strains associated with cancers. Vaccination is recommended for males starting at ages 11-12, but catch-up vaccinations are available for men up to age 45.
- Practicing safer sex: Using condoms or dental dams during sexual activity can reduce the risk of transmission, although not eliminate it entirely.
- Regular health check-ups: While there is no routine test for HPV in men, healthcare providers can identify visible symptoms and recommend screenings for related conditions.
- Strengthening the immune system: A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can enhance the body’s ability to fight off infections.
- Open communication: Discussing health statuses with partners can foster mutual understanding and responsibility.
Debunking Common Myths About HPV
Understanding the truths about HPV is vital to combat misinformation. Here are common myths debunked:
- Myth 1: HPV only affects women.
Truth: Men can also suffer from HPV-related health complications. - Myth 2: If I don’t see symptoms, I don’t have it.
Truth: Many HPV infections are asymptomatic, but they can still be transmitted. - Myth 3: Only those with risky lifestyles get HPV.
Truth: HPV is highly prevalent, and nearly everyone will encounter it. - Myth 4: Vaccines are unnecessary for men.
Truth: Vaccination is beneficial for all genders, reducing overall virus circulation.
Conclusion: Embracing Knowledge and Proactivity
The reality is that HPV is a common viral infection with profound implications for men’s health. By actively engaging in awareness, education, and preventive strategies, men can significantly lower their risks associated with HPV. Living with knowledge about HPV does not mean succumbing to fear; rather, it empowers individuals to make informed decisions that safeguard their health and the health of their partners. By treating HPV as a public health issue rather than a taboo, society can foster a culture of openness, reducing stigma and encouraging responsible health choices. Ultimately, through collective action and informed dialogue, we can work towards a future where HPV transmission is minimized, and individuals feel supported in addressing their health needs.