The Singhadurbar Fire: A Wake-Up Call for Digital Infrastructure Resilience
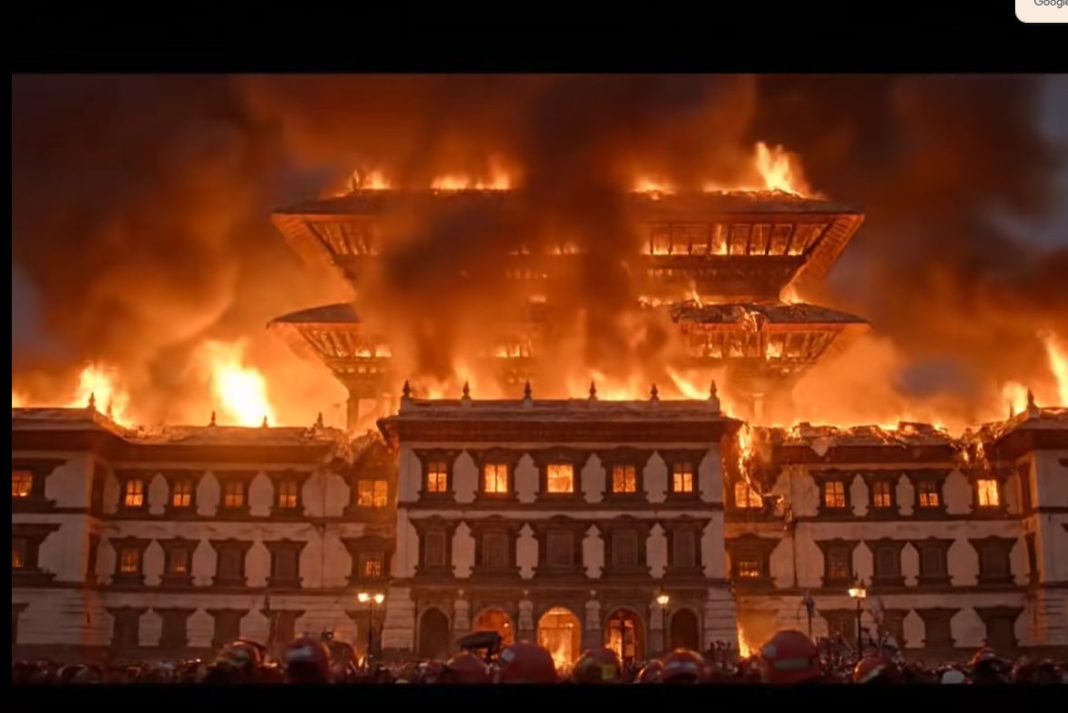
In September 2025, a significant incident unfolded in Kathmandu, Nepal, when a fire erupted within the historic Singhadurbar complex. This complex is not merely an architectural marvel; it serves as a pivotal hub that houses multiple government ministries and the national data center, which is the backbone of the country’s digital infrastructure. Initial assessments suggested that remarkably, the data center itself remained unharmed. However, this incident raised pressing concerns regarding the safety and durability of critical government systems, highlighting the vulnerabilities inherent in centralized data management.
The Incident and Its Immediate Aftermath
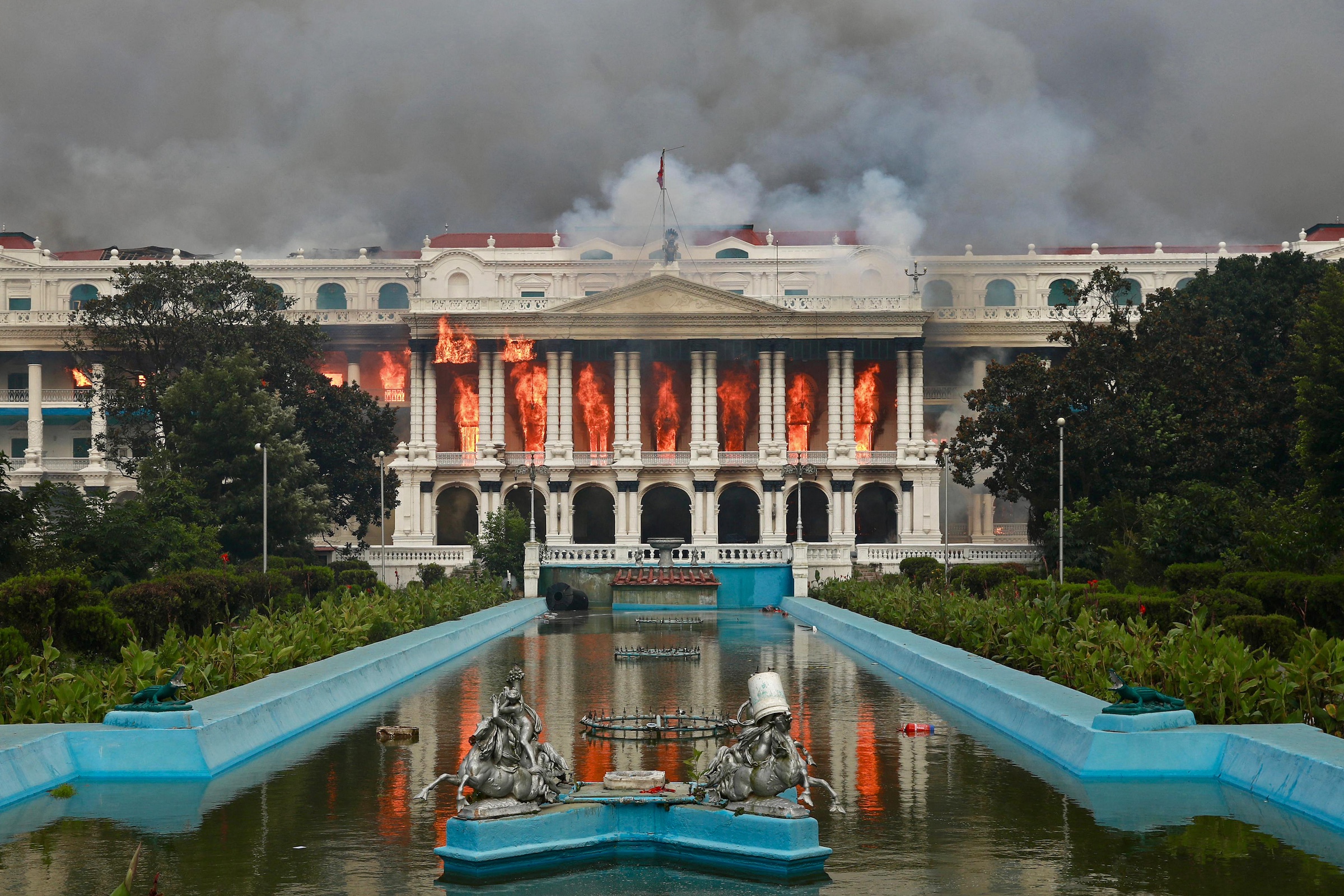
Reports from government officials and local media confirmed that the fire spread through various sections of the Singhadurbar complex, causing chaos and anxiety among workers and citizens alike. Emergency response teams were swiftly deployed to combat the flames, thereby protecting sensitive governmental facilities from further damage. While the Singhadurbar Data Center reportedly remained unharmed, the fire caused notable disruptions, damaging documents, archives, and workspaces across various ministries located within the complex. The incident raised alarms about the continuity of public services and the potential loss of critical data. Although officials quickly reassured the public that core systems were intact, the incident laid bare the fragility of centralized government infrastructure in the face of disasters.
In the immediate aftermath, the government launched an investigation to determine the cause of the fire, which was suspected to be linked to faulty electrical wiring. This incident prompted the need for urgent reviews of safety standards and protocols within government buildings. Citizens were left anxious about the situation, with many questioning the adequacy of fire safety measures in a building that houses vital national functions. The swift deployment of emergency services, while commendable, also highlighted the need for more comprehensive disaster readiness plans. In a nation where natural disasters are not uncommon, the fire at Singhadurbar was a stark reminder of how quickly things can deteriorate.
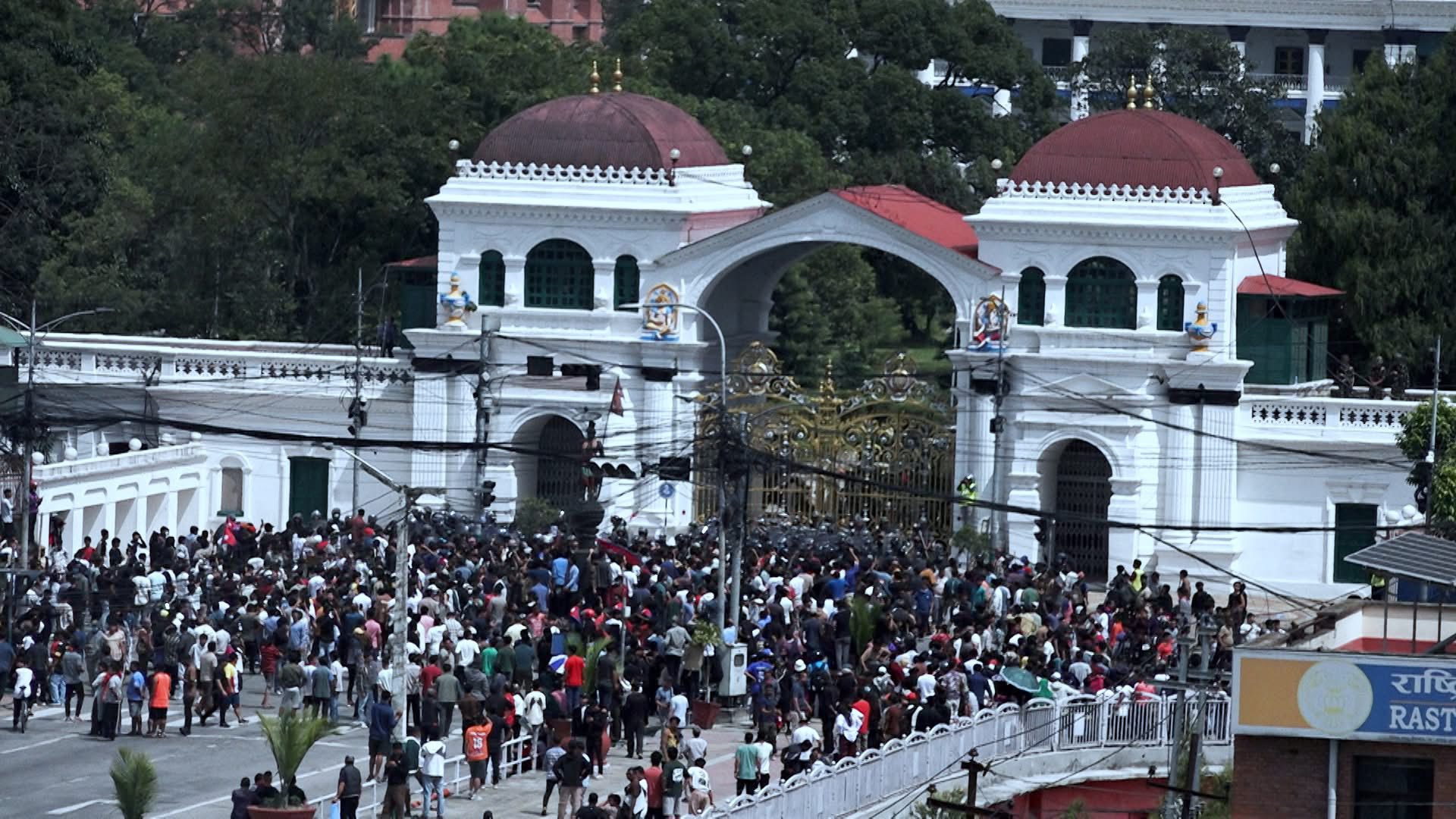
Understanding the Broader Implications
The significance of the Singhadurbar fire extends far beyond the immediate material damage and disruptions. It serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with storing vast amounts of national data within a single, centralized facility. One primary concern is the issue of vulnerability. When a nation keeps its essential records and databases confined to one location, it creates a single point of failure. In the event of catastrophic damage to that site, the impacts on public administration, law enforcement, and citizens’ civil rights could be dire.
Moreover, there is the potential for irreparable losses when it comes to historical and legal documents. Although many records are digitized, physical archives often contain irreplaceable information that cannot simply be recreated once lost. The fire underscores the necessity for comprehensive preservation strategies that ensure both digital and physical records are safeguarded against disasters. Furthermore, events of this nature can erode public trust; citizens expect their governments to protect sensitive information, ranging from property records to legal documentation. When such systems are threatened, even minimally, it prompts citizens to question the adequacy of existing safety measures, creating a rift between the government and the populace.
Key Lessons on Digital Resilience
The Singhadurbar fire offers several vital lessons for governments aiming to build resilient digital infrastructure. A crucial takeaway is the imperative of redundancy. Critical data should not be confined to one location; instead, it should be backed up in multiple, geographically dispersed centers to ensure continuous operation during local disasters. This approach minimizes the risk of total data loss and enhances recovery options in the event of catastrophic incidents.

Moreover, the role of prevention systems cannot be overstated. Data centers require advanced fire detection and suppression technologies, alongside stringent safety protocols to minimize risk. Infrastructure must be designed in such a way that a fire in one section does not easily spread to areas housing essential systems. For instance, incorporating firewalls, fire-resistant materials, and advanced HVAC systems can significantly mitigate risks. Additionally, governments can substantially benefit from developing comprehensive disaster recovery plans. Regular drills, system audits, and backup restoration exercises can significantly enhance preparedness for unforeseen events.
The integration of hybrid solutions, combining on-site servers with secure cloud storage, adds another layer of resilience. This dual approach not only protects against localized disasters but also ensures data accessibility from various locations. Effective communication is equally critical; following the Singhadurbar fire, officials promptly clarified that the data center remained undamaged, which helped mitigate misinformation and reassured the public. Such transparency during crises fosters trust and accountability—an essential component for public confidence in governmental institutions.
Moving Forward: Strengthening Infrastructure in Nepal
As Nepal begins to recover from this incident, the government faces the pressing challenge of reinforcing its infrastructure. This includes conducting a thorough assessment of the fire’s impact, repairing affected offices, and modernizing fire safety systems within the Singhadurbar complex. Additionally, revisiting data protection policies, improving legal frameworks, and establishing new standards for the storage and security of sensitive information will be paramount. This fire incident is likely to catalyze broader discussions about how nations safeguard their national data assets, particularly in an era where digital governance is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Furthermore, establishing partnerships with cybersecurity firms and technology experts can provide the government with the necessary resources and knowledge to bolster their infrastructure against future threats. Engagement with international bodies that specialize in disaster management and infrastructure resilience can also yield valuable insights and best practices. The Singhadurbar fire is not merely an isolated incident; it signifies a crucial turning point for Nepal’s approach to digital governance, urging policymakers to prioritize infrastructure that can withstand both man-made and natural disasters.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Vigilance and Preparedness
While the Singhadurbar fire did not result in the catastrophic loss that many feared, it serves as a crucial reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in centralized government systems. Protecting sensitive data is just as much about cybersecurity as it is about physical safety. Governments around the world can glean valuable insights from this incident, adopting stronger disaster-preparedness strategies to ensure that public trust and essential services remain intact, even amid unforeseen crises. The lessons learned from the Singhadurbar complex will resonate through the corridors of governance, prompting a re-evaluation of how nations can fortify their digital infrastructures against future threats.