**Tragic Case of Blindness Highlights Dangers of Sleeping with Contact Lenses**
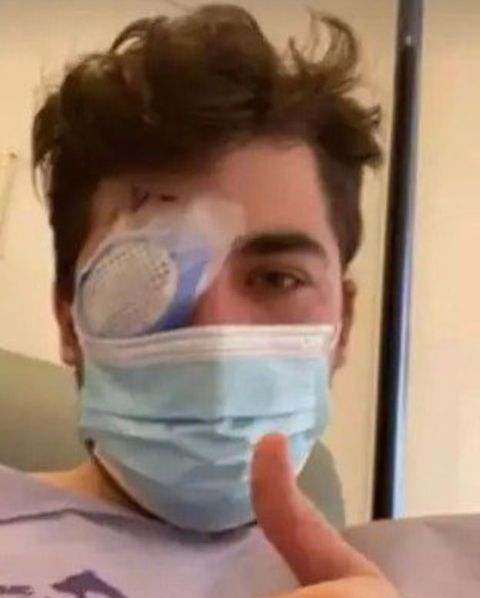
A shocking and heartbreaking story has emerged about a man who lost his sight after sleeping with his contact lenses on overnight. At 39 years old, the man, identified as Groeschen, is now permanently blind in one eye due to a serious bacterial infection caused by the improper use of his lenses. His case serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with wearing contact lenses overnight, as experts warn that it can lead to severe and sometimes irreversible damage to the eyes.
Groeschen’s story began like many others—he was simply trying to make his life more convenient by wearing contact lenses throughout the day and night. However, what started as a common mistake turned into a nightmare when he developed an eye infection. The infection, caused by a bacterium called *Pseudomonas*, rapidly worsened and led to the formation of a painful corneal ulcer. Despite treatment efforts, the damage was too severe, and Groeschen was left with permanent vision loss in his affected eye.
Doctors have long warned against the practice of sleeping with contact lenses in, as it significantly increases the risk of eye infections. When lenses are worn overnight, they restrict the flow of oxygen to the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface of the eye. This can create an environment where bacteria and other harmful pathogens thrive, leading to infections that can quickly spiral out of control.
Pseudomonas, the bacterium that caused Groeschen’s infection, is particularly dangerous. It is one of the most common culprits behind severe eye infections, and it can lead to rapid tissue damage if not treated properly. In some cases, like Groeschen’s, the infection can cause permanent scarring or vision loss, even with aggressive medical intervention.
Groeschen’s case serves as an important cautionary tale about the need for proper care and maintenance of contact lenses. Experts emphasize the importance of removing contact lenses before sleeping, following recommended cleaning procedures, and regularly replacing lenses to prevent infection and other complications. In addition, individuals should always consult with their eye care provider about the best practices for contact lens use and to ensure they are using lenses that are suitable for their specific needs.
This story is a powerful reminder that while contact lenses offer convenience and comfort, they must be handled with care. Failing to follow proper guidelines can lead to serious, life-altering consequences. Groeschen’s experience is a tragedy, but it’s also an opportunity to educate others about the risks associated with contact lens misuse—and the critical importance of eye health and safety.
For anyone who wears contact lenses, taking the proper precautions could be the difference between clear sight and irreversible blindness.